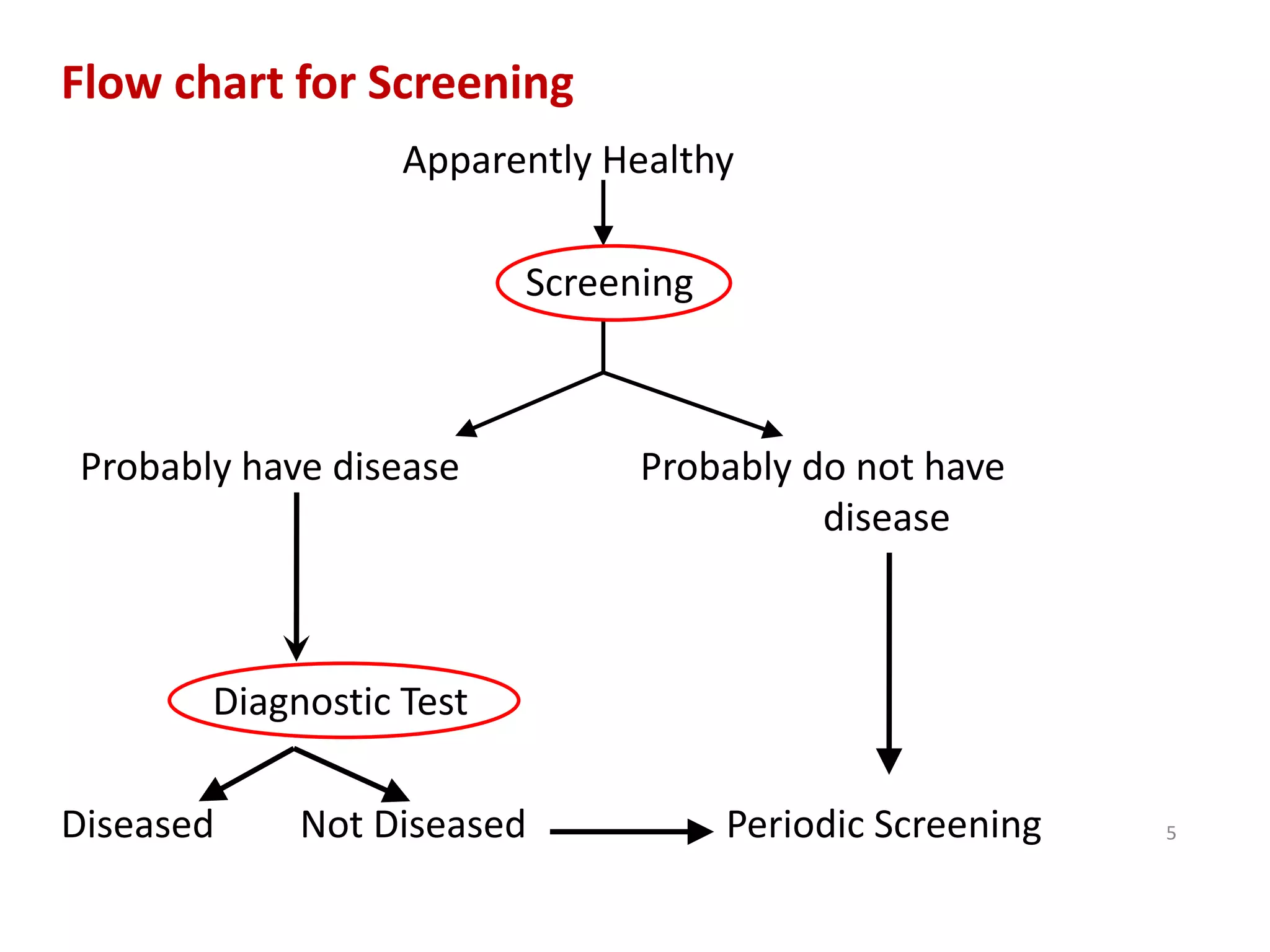
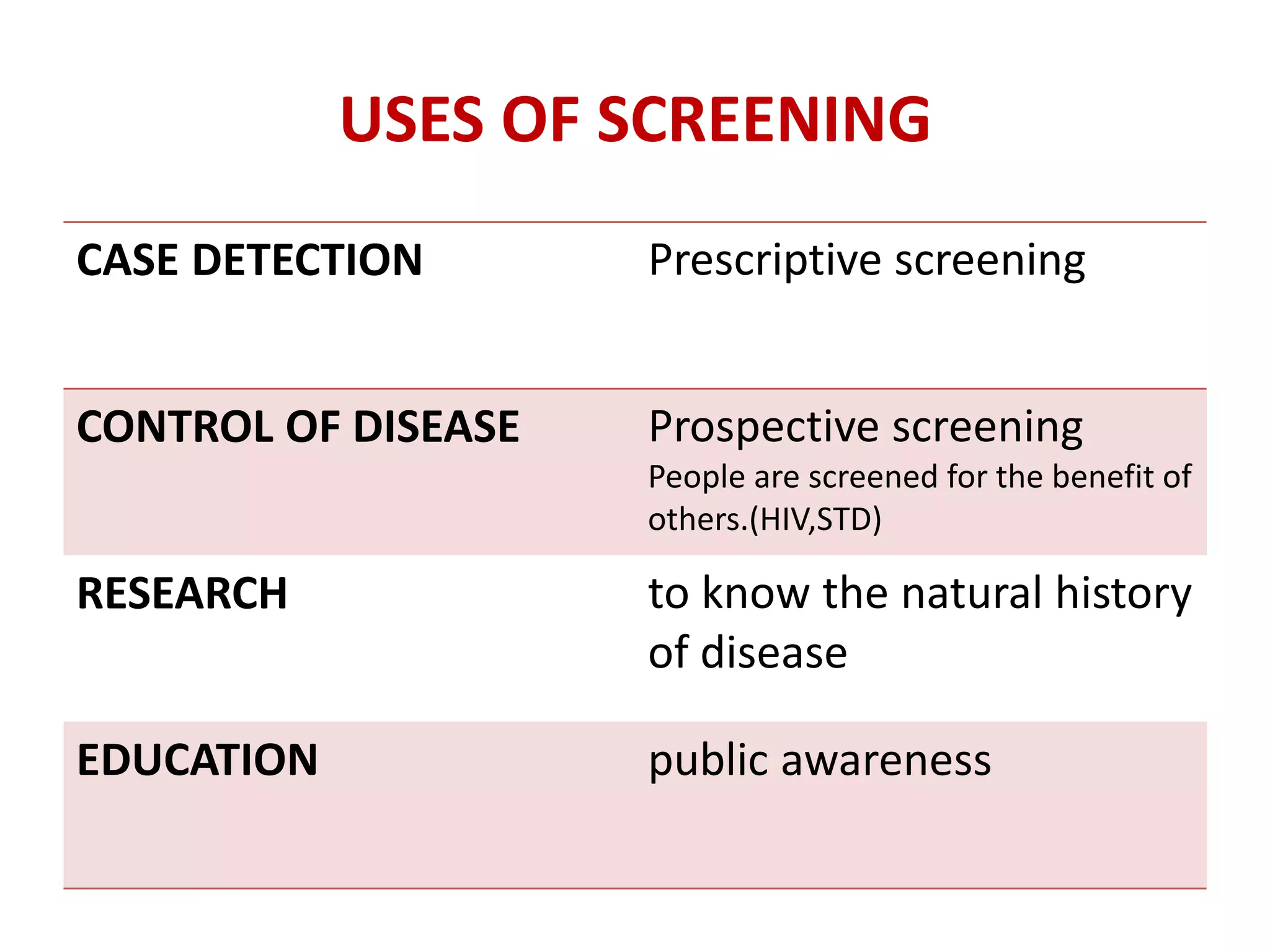
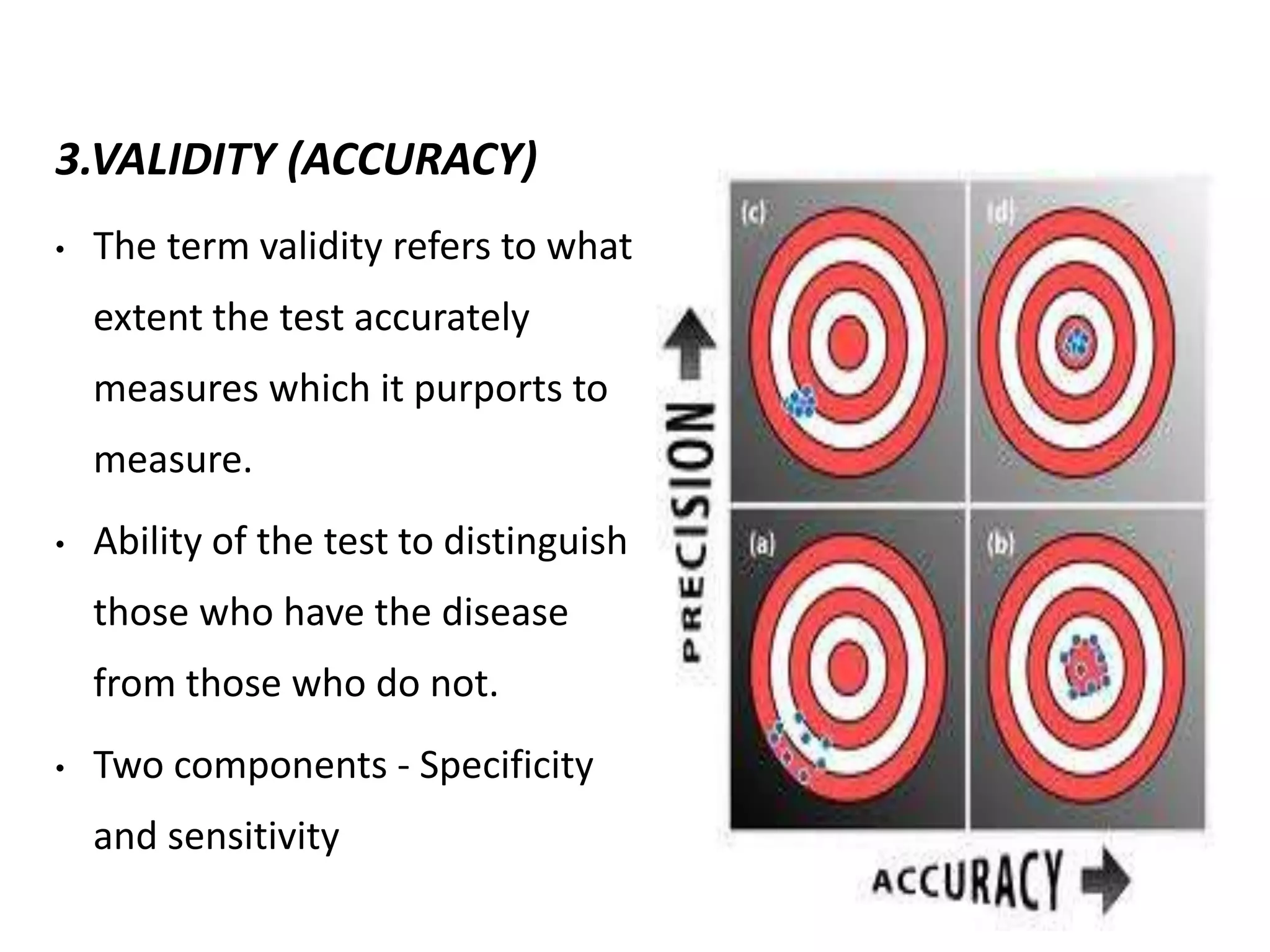
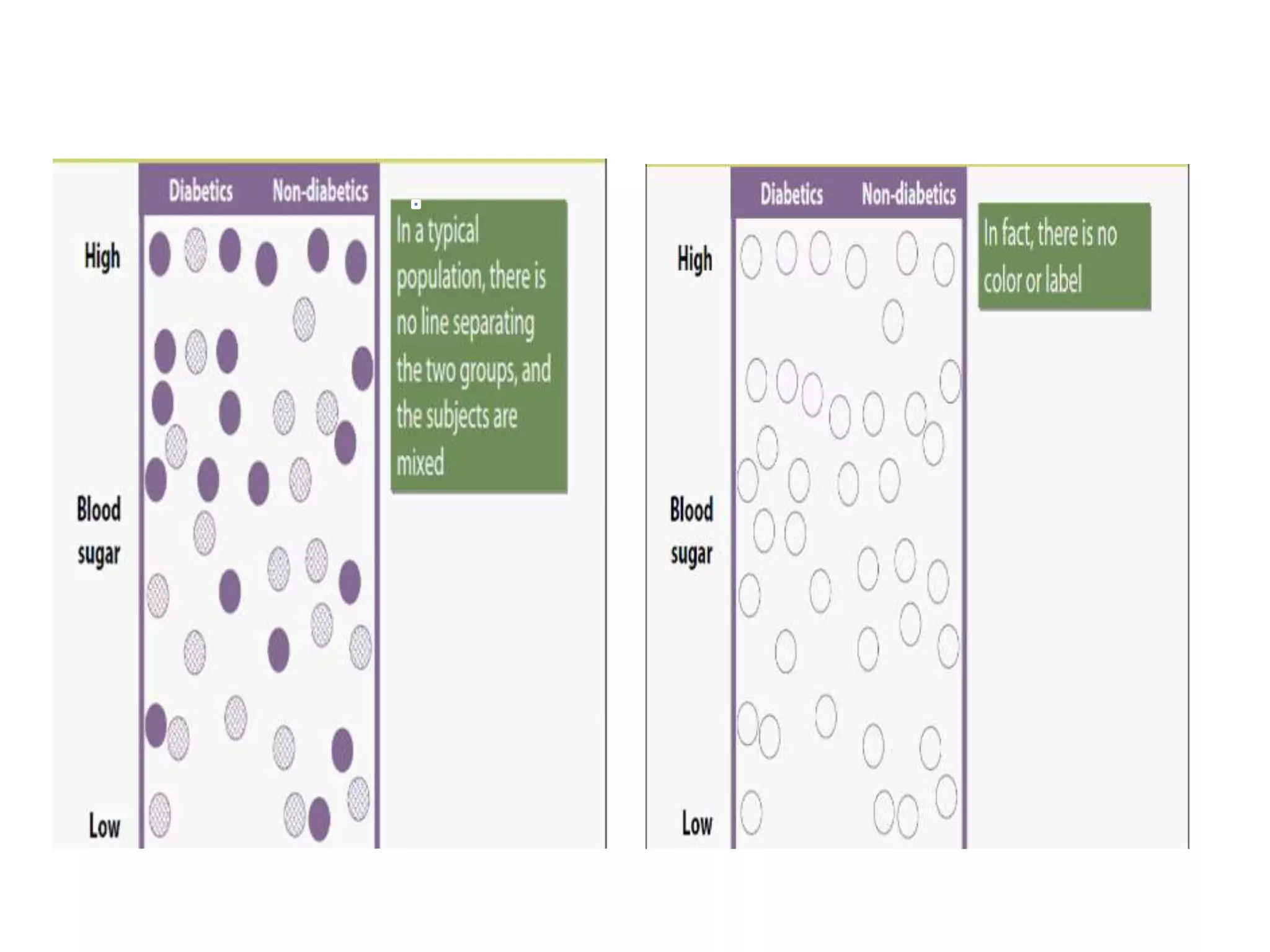
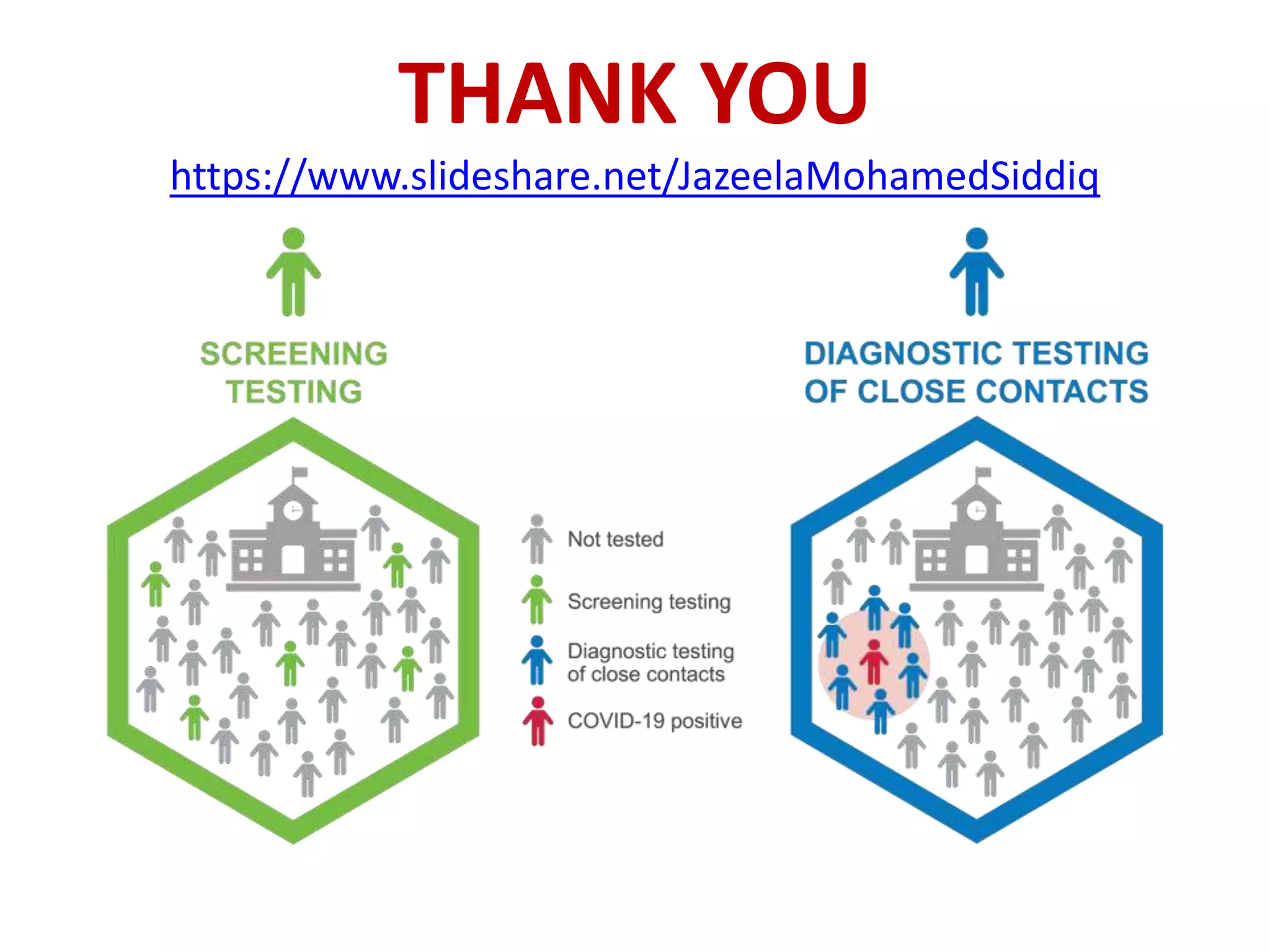
Screening involves testing apparently healthy individuals to detect unrecognized disease. It aims to identify disease at earlier, more treatable stages through simple, rapid and low-cost tests. An ideal screening test should accurately detect the target condition, have a high yield of positive results, and be acceptable to the population. Screening criteria include addressing an important health problem, having a recognizable pre-symptomatic stage, and providing early treatment that reduces disease burden. Evaluation of screening tests considers their sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values to determine how well results identify individuals with and without the disease. The cut-off point for positive results impacts the balance between false positives and negatives.