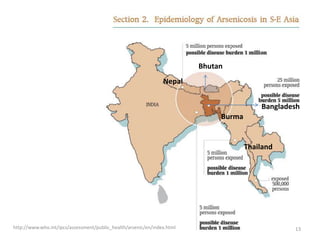
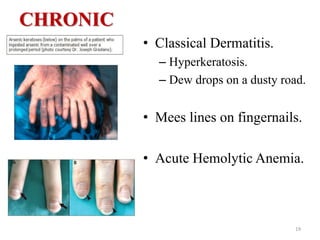
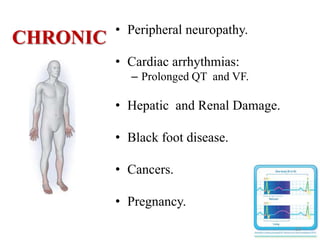
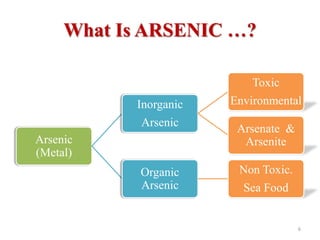
Arsenic is commonly found in groundwater and can cause serious health effects. The document discusses arsenic's properties, major sources like groundwater, and health impacts like skin lesions and cancers. It also provides information on limits and standards, noting the WHO drinking water guideline of 10 μg/L, as well as strategies for control and prevention like installing arsenic removal systems and educating the public.









![Burden of Arsenic Poisoning.
• United States
–(AAPCC) & (NPDS) in 2010:
• 927 human exposures.
• The majority of the pesticide exposures occurred in
children younger than 5 years (43 [65%] of 67).
Bronstein AC, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR Jr, Green JL, Rumack BH, Dart RC. 2010 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison
Control Centers' National Poison Data System (NPDS): 28th Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). Dec 2011;49(10):910-41.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arsenic-130515113400-phpapp02/85/Arsenic-11-320.jpg)