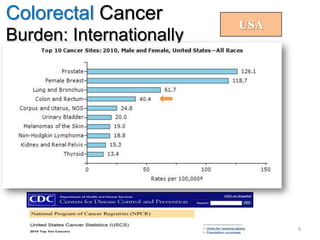
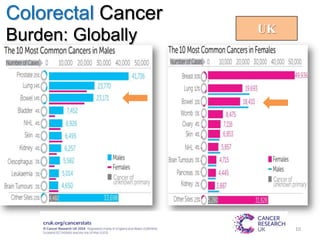
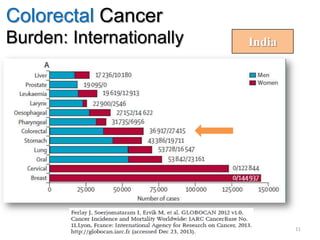
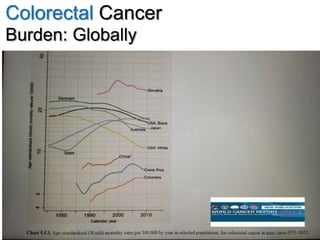
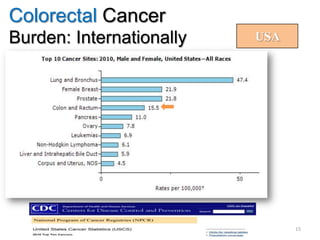
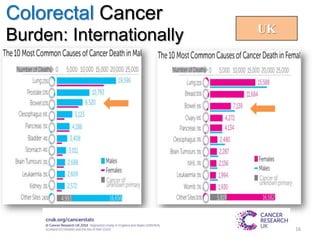
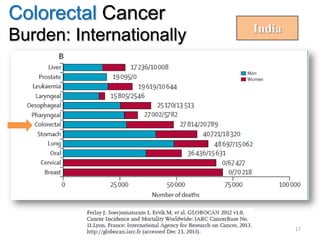
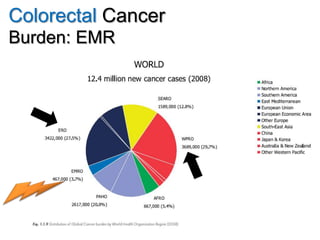
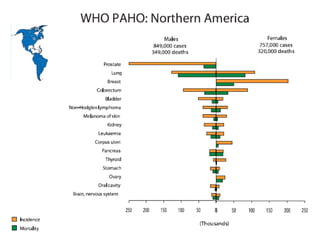
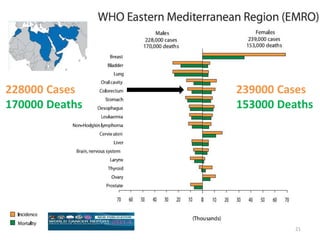
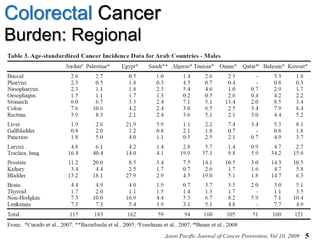
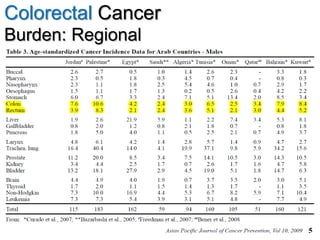
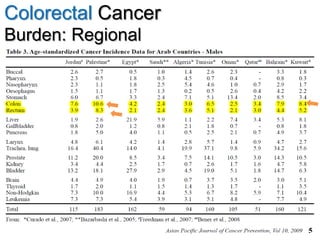
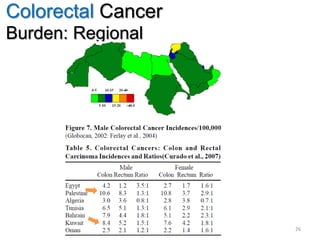
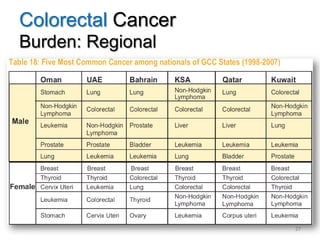
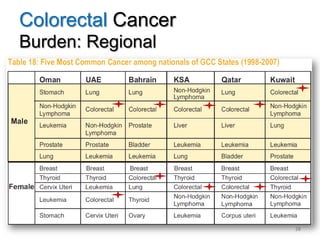
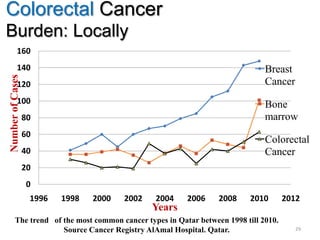
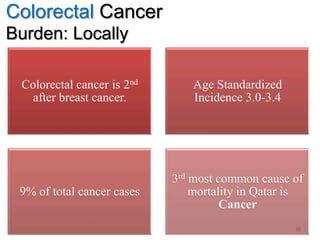
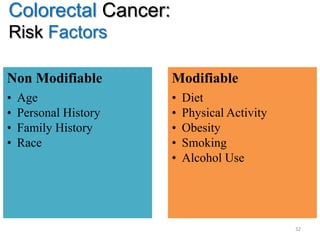
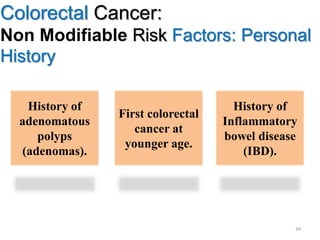
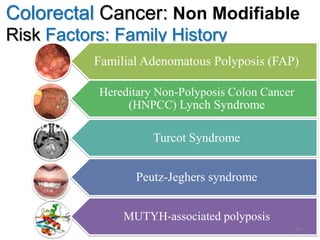
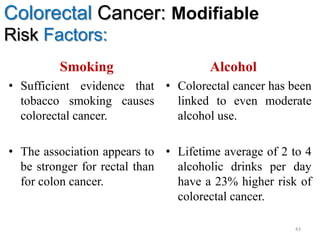
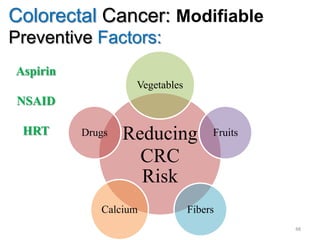
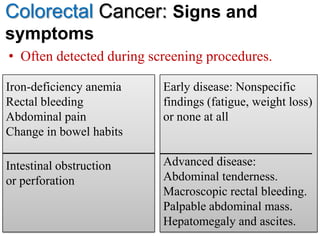
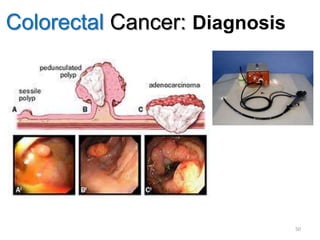
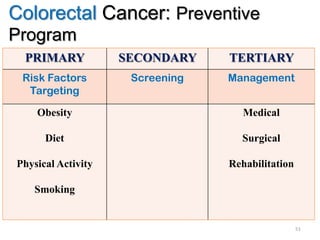
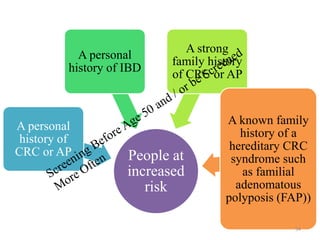
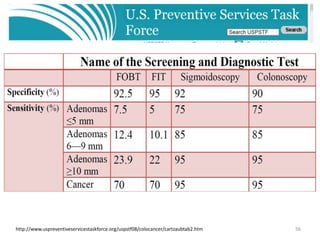
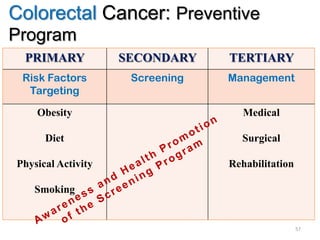
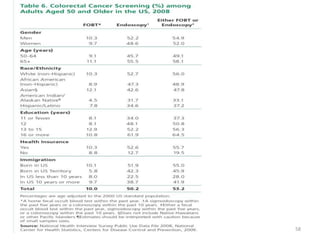
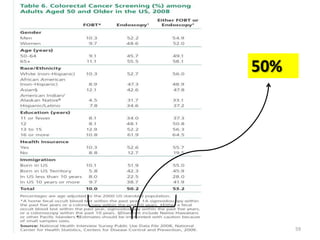
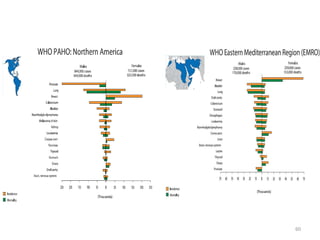
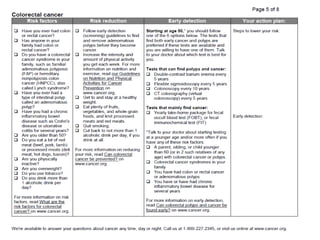
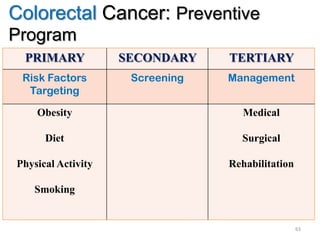
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common and fatal cancers globally. Risk factors include age, family history, diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity. Screening tests like colonoscopy can detect and remove precancerous polyps, helping to prevent colorectal cancer by interrupting its typical development through the adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Modifying lifestyle factors and participating in screening are important for colorectal cancer prevention and early detection.