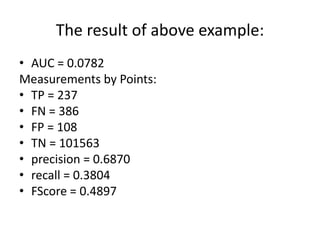
This document provides an overview and tutorial of the Weka machine learning software. It discusses what Weka is, the types of tasks it can perform like data preprocessing, classification, clustering, and visualization. It also provides suggestions on how Weka can help with homework assignments. Specific components of Weka are described, like the Explorer interface and different classifiers. The document also includes code examples for loading data, applying filters, building classifiers, and evaluating models using cross-validation. It concludes with an explanation and example of calculating the FROC performance metric.






![filters
import weka.core.Instances;
import weka.filters.Filter;
import weka.filters.unsupervised.attribute.Remove;
...
String[] options = new String[2];
options[0] = "-R"; // "range"
options[1] = "1"; // first attribute
Remove remove = new Remove(); // new instance of filter
remove.setOptions(options); // set options
remove.setInputFormat(data); // inform filter about dataset AFTER
setting options
Instances newData = Filter.useFilter(data, remove); // apply filter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saihw1wekatutorialpptx-machine-discovery-and-social-network2363/85/saihw1_weka_tutorial-pptx-Machine-Discovery-and-Social-Network-9-320.jpg)
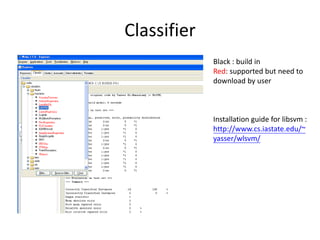
![classifier
import weka.classifiers.functions.LibSVM;
...
String[] options = String[] options =
weka.core.Utils.splitOptions("-S 0 -K 2 -D 3 -G 0.0 -R 0.0 -N 0.5
-M 40.0 -C 1.0 -E 0.0010 -P 0.1 -B");
LibSVM classifier = new LibSVM(); // new instance of tree
classifier.setOptions(options); // set the options
classifier.buildClassifier(data); // build classifier](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saihw1wekatutorialpptx-machine-discovery-and-social-network2363/85/saihw1_weka_tutorial-pptx-Machine-Discovery-and-Social-Network-10-320.jpg)
![Classifying instances
Instances unlabeled=…//load from somewhere
…
for (int i = 0; i < unlabeled.numInstances(); i++) {
Instance ins=unlabeled.instance(i);
clsLabel = classifier.classifyInstance(ins); //get predict label
double[] prob_array=classifier.distributionForInstance(ins);
//get probability for each category
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saihw1wekatutorialpptx-machine-discovery-and-social-network2363/85/saihw1_weka_tutorial-pptx-Machine-Discovery-and-Social-Network-11-320.jpg)
![Example:weka+libsvm+5 folds CV
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
PrintWriter pw_score=new PrintWriter( new FileOutputStream ("c:tempscore.txt"));
PrintWriter pw_label=new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream ("c:templabel.txt"));
PrintWriter pw_pid=new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream ("c:temppid.txt"));
Instances data = new Instances(
new BufferedReader(
new FileReader("C:tempTrainSet_sn.arff")));
Remove remove = new Remove(); // new instance of filter
remove.setOptions(weka.core.Utils.splitOptions("-R 2-11,129"));// set options
remove.setInputFormat(data); // inform filter about dataset AFTER setting options
Int seed = 2; // the seed for randomizing the data
int folds = 5; // the number of folds to generate, >=2
data.setClassIndex(0); // first attribute is groundtruth
Instances randData;
Random rand = new Random(seed); // create seeded number generator
randData = new Instances(data); // create copy of original data
randData.randomize(rand); // randomize data with number generator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saihw1wekatutorialpptx-machine-discovery-and-social-network2363/85/saihw1_weka_tutorial-pptx-Machine-Discovery-and-Social-Network-12-320.jpg)
![for(int n=0;n<folds;n++){
Instances train = randData.trainCV(folds, n);
Instances test = randData.testCV(folds, n);
System.out.println("Fold "+n+"train "+train.numInstances()+"test "+test.numInstances());
String[] options = weka.core.Utils.splitOptions("-S 0 -K 2 -D 3 -G 0.0 -R 0.0 -N 0.5 -M 40.0 -C
1.0 -E 0.0010 -P 0.1 -B");
LibSVM classifier=new LibSVM();
classifier.setOptions(options);
FilteredClassifier fc = new FilteredClassifier();
fc.setFilter(remove);
fc.setClassifier(classifier);
fc.buildClassifier(train);
for(int i=0;i<test.numInstances();i++)
{
double[] tmp=(double[])fc.distributionForInstance(test.instance(i));
//tmp[0] :prob of negtive
//tmp[1] :prob of positive
pw_label.println(test.instance(i).attribute(0).value((int)test.instance(i).value(0))); //ground
truth
pw_score.println(tmp[1]); //predict value
pw_pid.println((int)test.instance(i).value(4)); //study-ID
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saihw1wekatutorialpptx-machine-discovery-and-social-network2363/85/saihw1_weka_tutorial-pptx-Machine-Discovery-and-Social-Network-13-320.jpg)
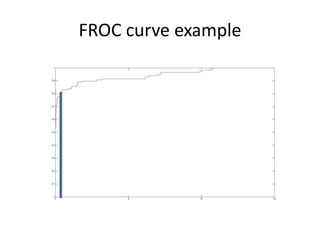
![FROC
Algorithm:
1. Load “predicted score”, “ground truth”, and “patient id”.
2. Initialize :
“Detected_patients = [ ]
Sorting rows
( priority “predicted score” > “ground truth” > “patient id” in descending order).
3. For each row,
If ground truth is negative, x+=1
Else // get a positive point
If patient is not in “Detected_patients, //get a new positive patient
y+=1 and add patient_id to Detected_patients
else //patient is found before
do nothing
4. Normalize
x => 0~ average false alarm per image i.e. X is divided by total image numbers
y => 0~1 i.e. Y is divided by patients numbers
5. Calculate the area under the curve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saihw1wekatutorialpptx-machine-discovery-and-social-network2363/85/saihw1_weka_tutorial-pptx-Machine-Discovery-and-Social-Network-14-320.jpg)

![FROC tools-Matlab
• Matlab matlab function
– [Pd_patient_wise,FA_per_image,AUC] =
get_ROC_KDD(p,Y,PID,fa_low,fa_high)
• Pd_patient_wise
– The y location of each point on the curve.
• FA_per_image
– The x location of each point on the curve.
• AUC
• p – Predicted label
• Y – Ground truth
• PID – Patient ID
– Plot(FA_per_image,Pd_patient_wise);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saihw1wekatutorialpptx-machine-discovery-and-social-network2363/85/saihw1_weka_tutorial-pptx-Machine-Discovery-and-Social-Network-16-320.jpg)