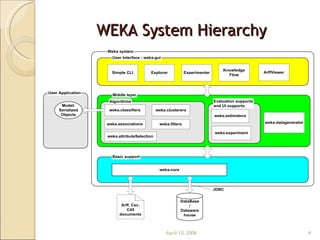
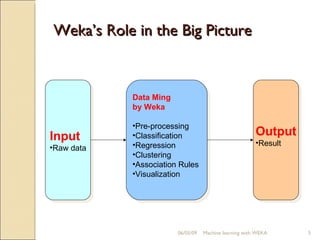
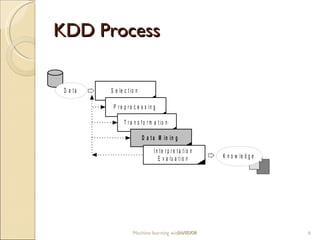
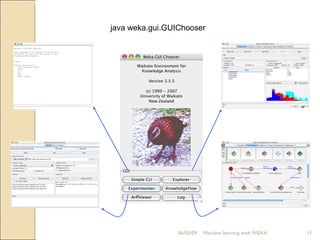
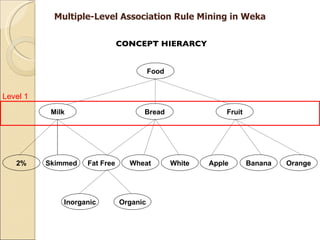
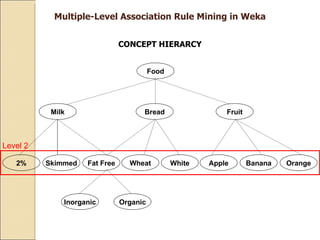
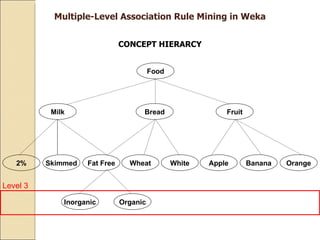
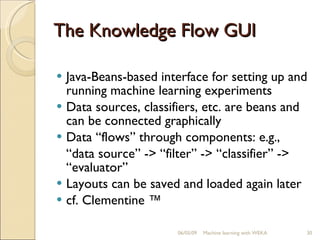
This document provides an overview of WEKA, a popular open-source machine learning software. WEKA contains tools for data pre-processing, classification, regression, clustering, association rule mining, and visualization. It was initially developed at the University of Waikato and is now maintained by the machine learning community. The document describes WEKA's main components, algorithms, and graphical user interfaces for exploring data and building machine learning models. It also briefly discusses WEKA's history and current uses in research.