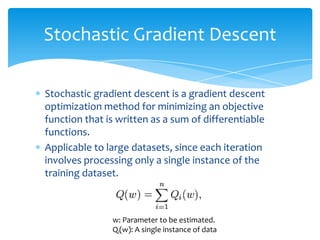
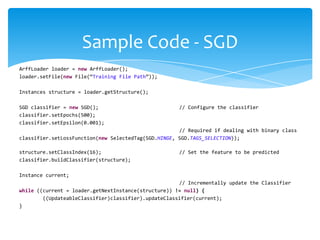
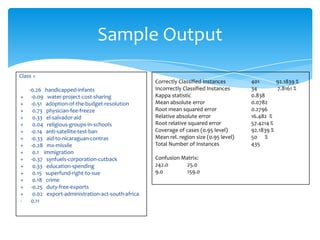
The document provides an overview of incremental learning using Weka, a machine learning software for data mining. It describes the process of training updateable classifiers, utilizing stochastic gradient descent for optimizing large datasets, and includes sample code, results, and challenges faced. The presentation is guided by Dr. Tran and explains key concepts and steps involved in implementing and evaluating models with Weka.