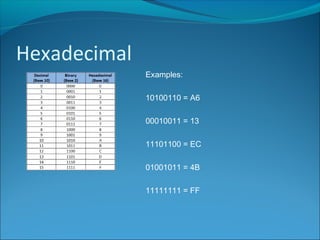
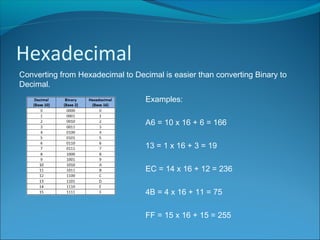
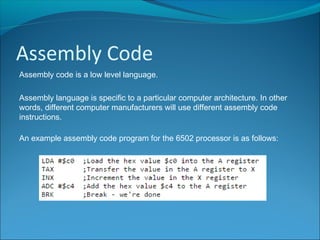
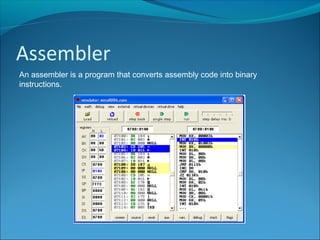
Machine code consists of binary instructions that are directly executed by the CPU. Each instruction performs a specific task like loading a value or adding numbers. Hexadecimal is typically used instead of binary by programmers because it is easier to convert binary to hexadecimal than to decimal. Hexadecimal is base 16, so it uses 16 symbols (0-9 and A-F) to represent values. Assembly code is a low-level language that is specific to a particular computer architecture. An assembler converts assembly code into binary machine code instructions. Assembly code runs very fast but is dependent on the processor and difficult to learn and port between systems.