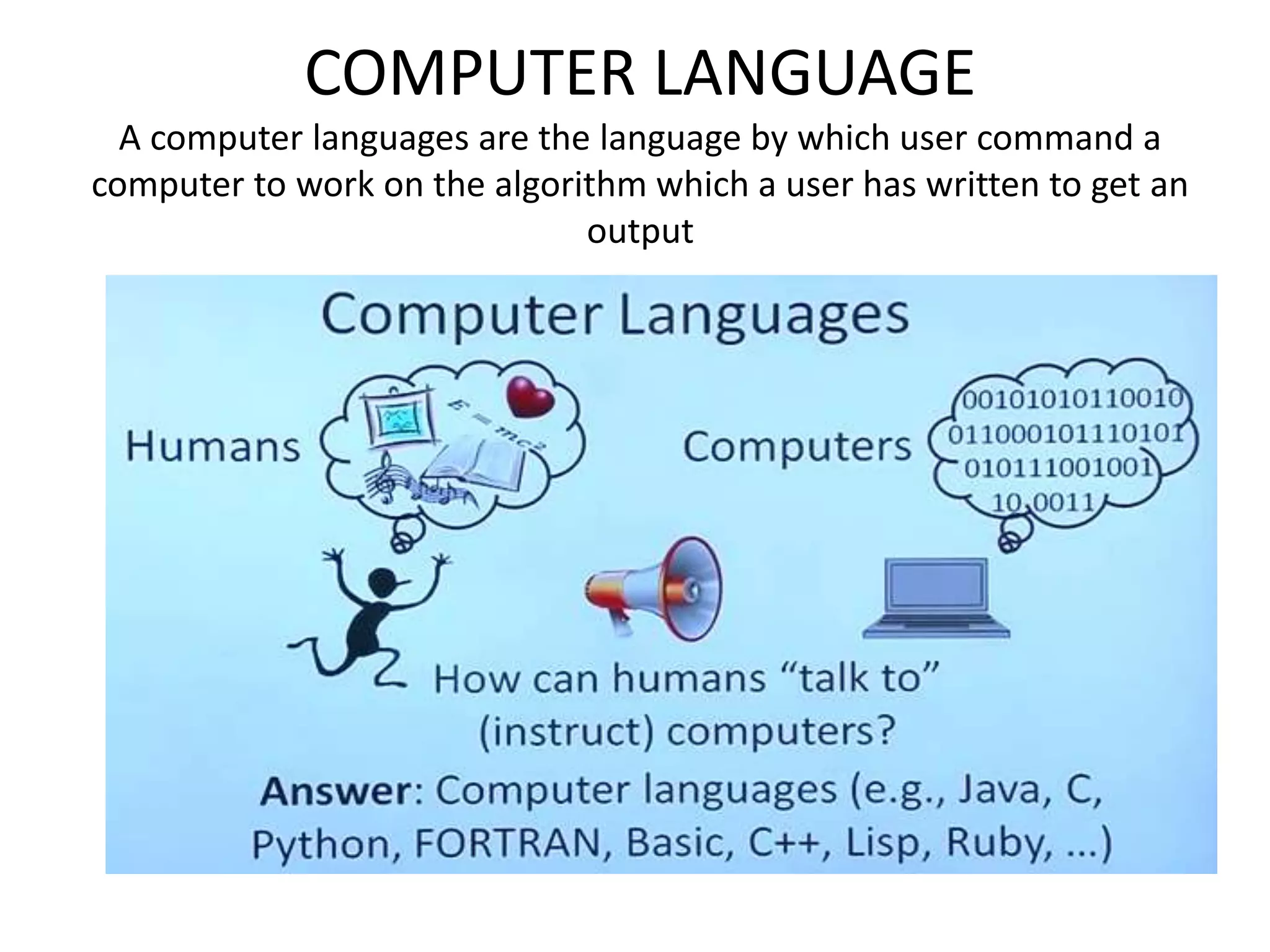
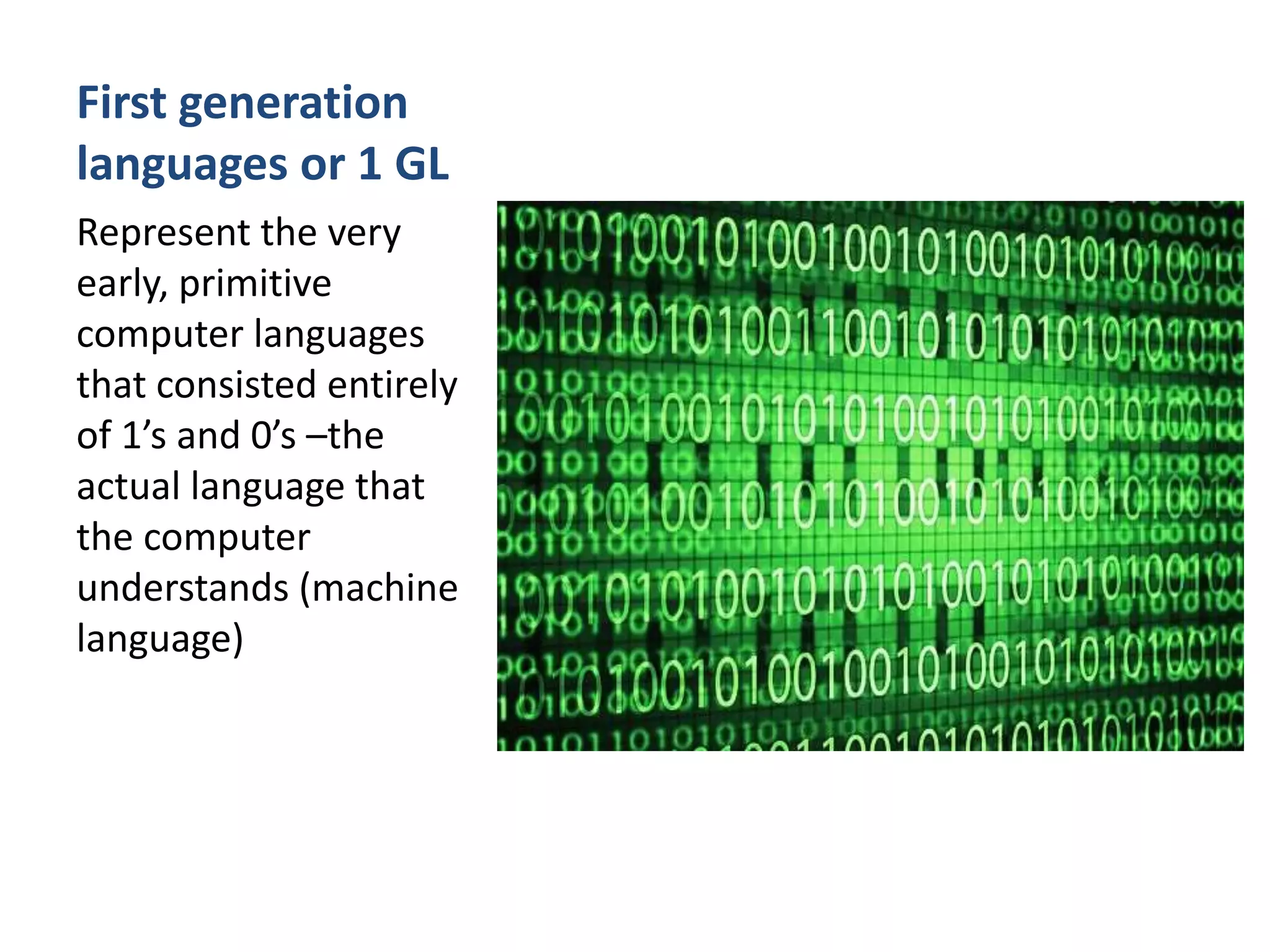
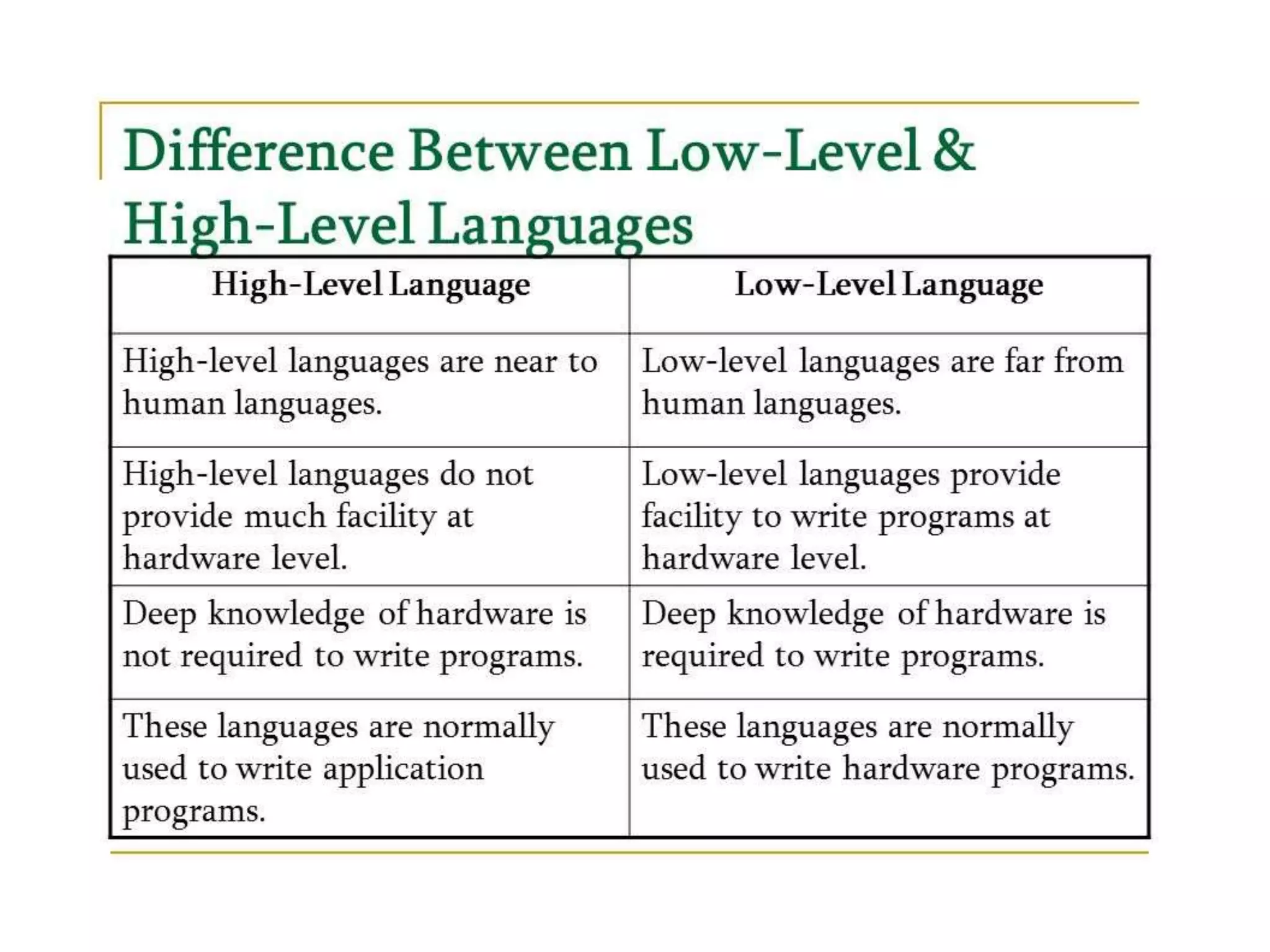
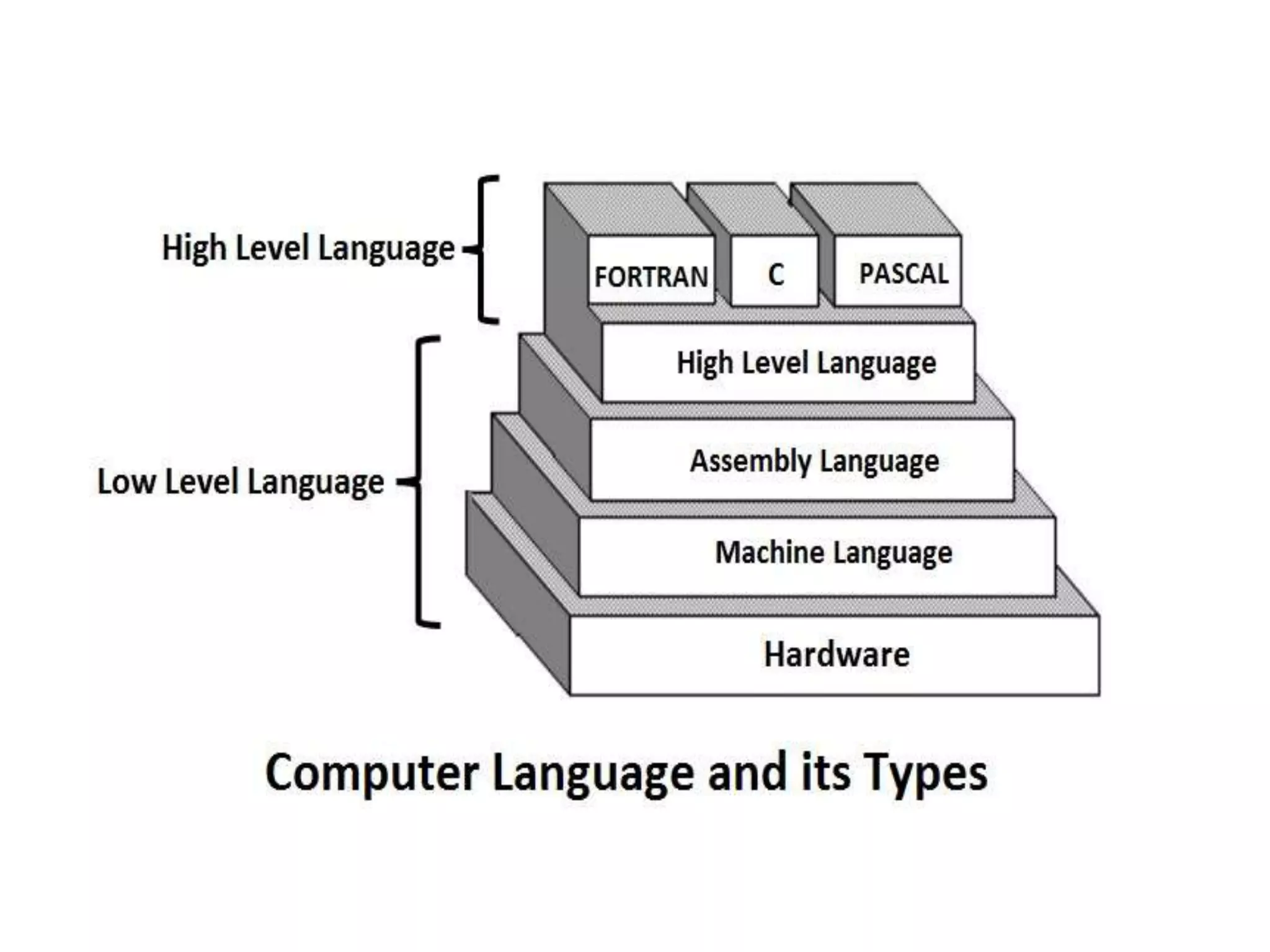
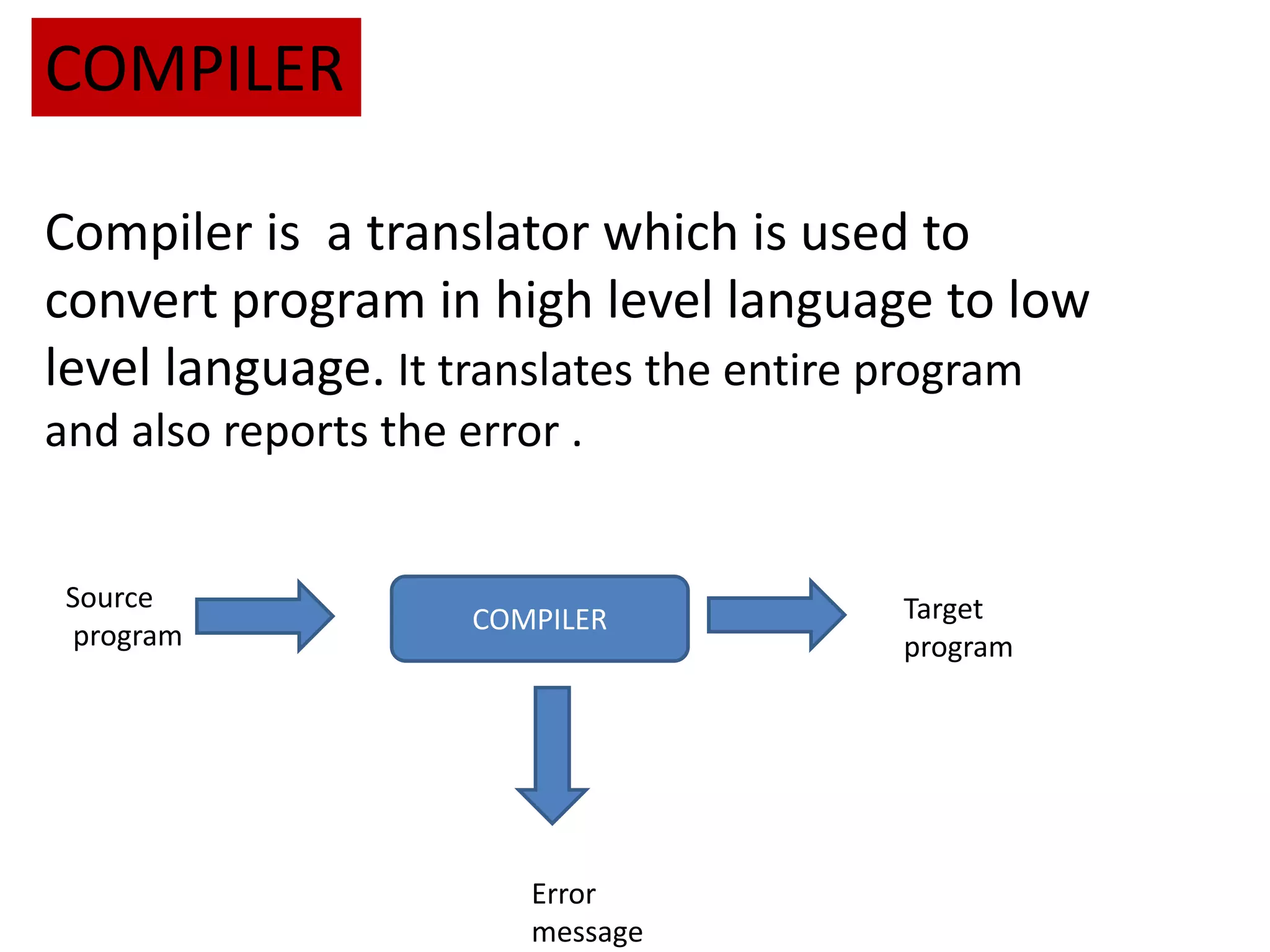
The document explains the concept of computer languages, distinguishing between low-level and high-level languages. It details the evolution of languages from first generation (machine language) to fifth generation, which includes various programming languages and their unique characteristics. Additionally, it describes the role of translators, such as assemblers, interpreters, and compilers, in converting high-level language into machine-readable code.