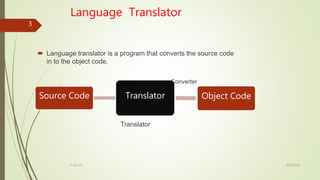
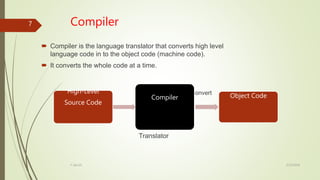
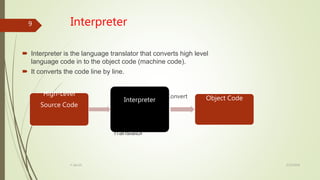
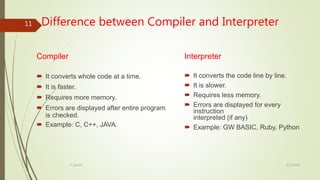
The document discusses different types of language translators including compilers, interpreters, and assemblers. A language translator converts source code into object code that computers can understand. Compilers convert an entire program into object code at once, while interpreters convert code line-by-line. Compilers are generally faster but require more memory, and errors are detected after compilation. Interpreters are slower but use less memory and can detect errors as they interpret each line.