There are three main types of computer languages:
1. Machine language - Understood directly by computers as binary, fast but difficult for humans.
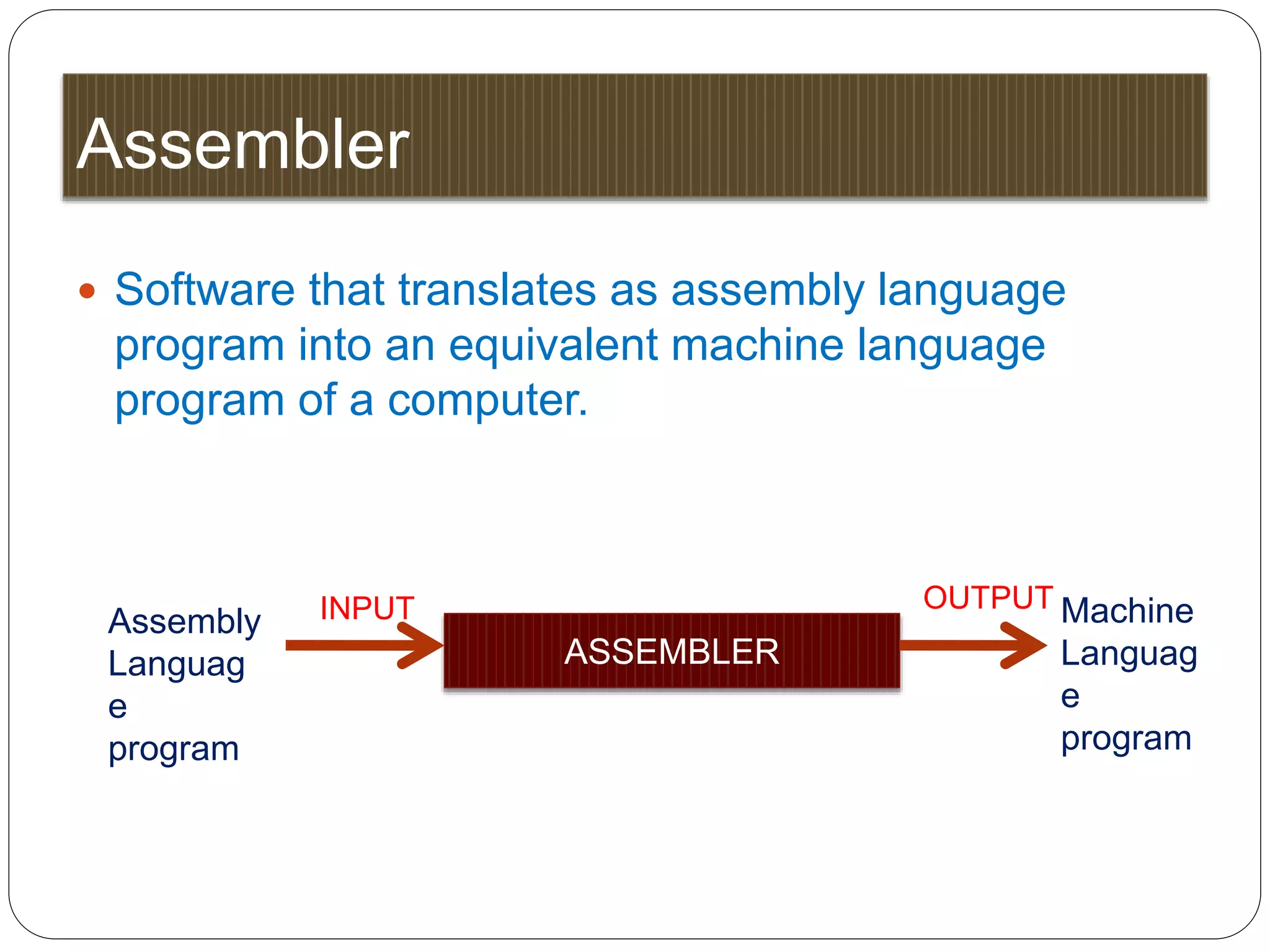
2. Assembly language - Uses mnemonics like ADD instead of binary, easier for humans but still machine-dependent. Requires an assembler to translate to machine language.
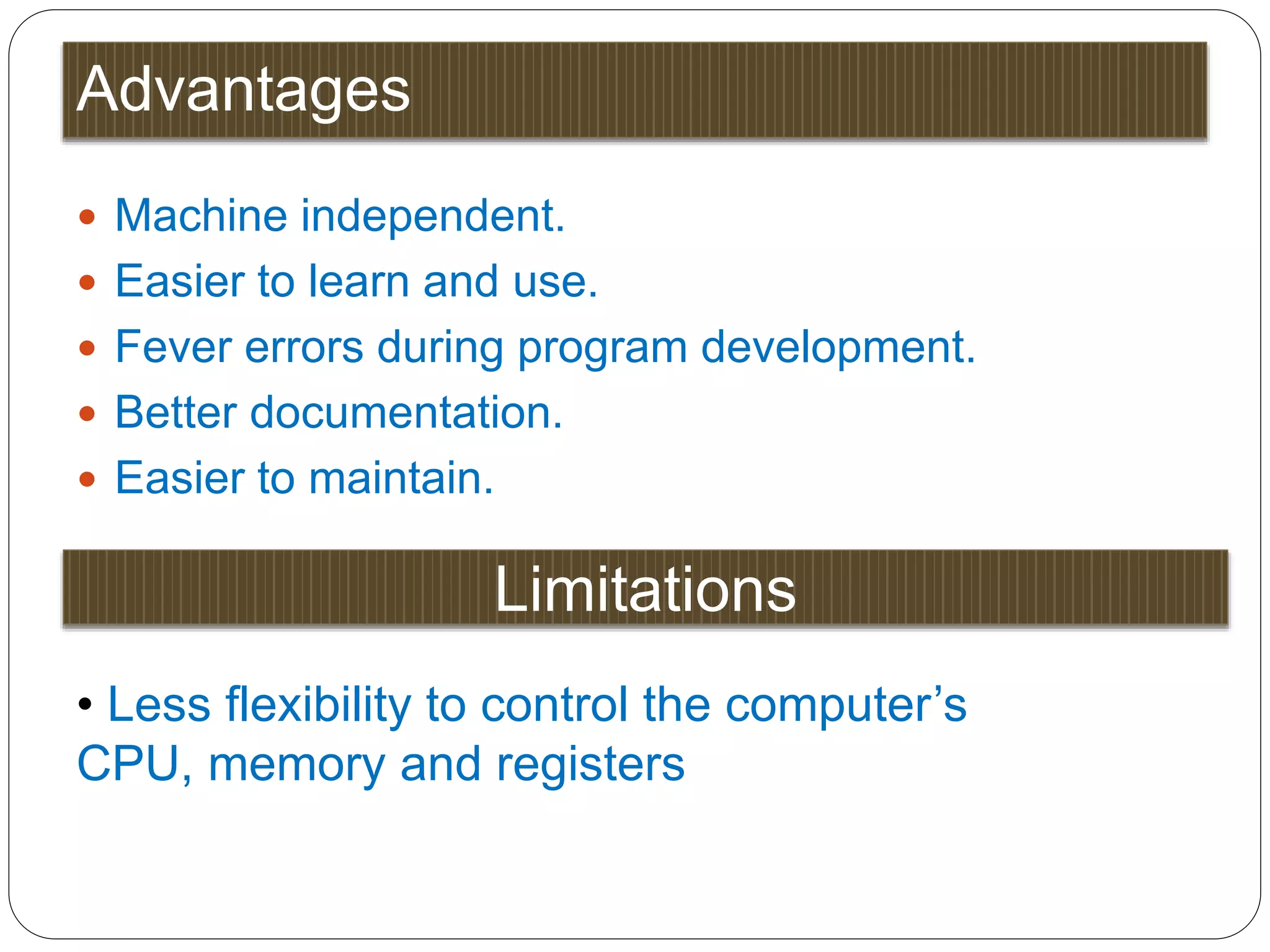
3. High-level languages - Are machine independent, use familiar words and symbols, and require compilers or interpreters to translate to machine language. They are easier for programmers but provide less control over hardware.