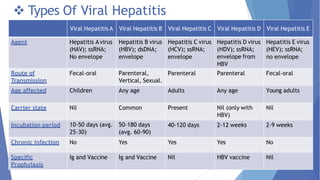
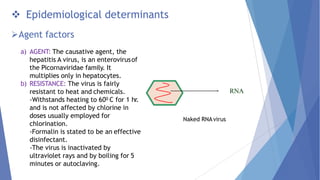
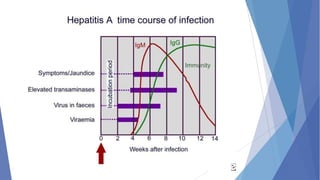
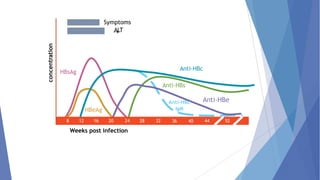
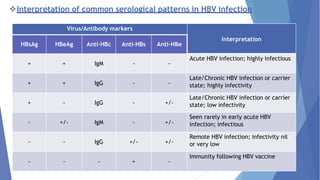
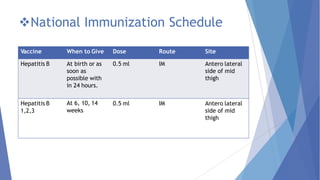
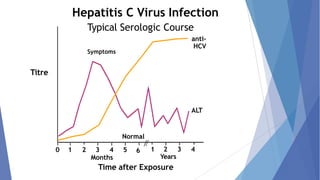
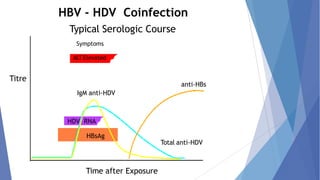
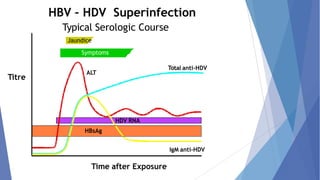
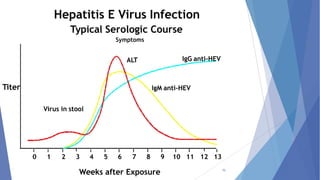
Viral hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver caused by viruses. The five main types are Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Hepatitis A is transmitted through the fecal-oral route while Hepatitis B, C, and D are transmitted through blood or bodily fluids. Acute viral hepatitis causes symptoms for less than 6 months while chronic hepatitis lasts over 6 months and can lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer over time if left untreated.