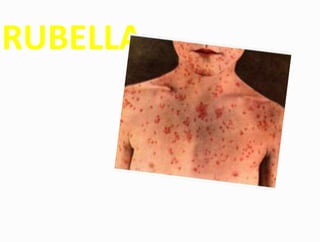
Rubella, also known as German measles, is a mild childhood infection caused by the rubella virus. It is typically a mild disease lasting 1-3 days, though infection during pregnancy can cause serious complications for the fetus. The virus is transmitted through respiratory droplets. Diagnosis is made through virus isolation or serological tests. There is no specific treatment, though vaccination provides effective prevention.