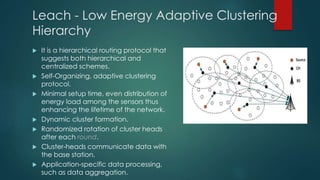
The document discusses routing protocols in wireless sensor networks (WSNs), categorizing them into flat, hierarchical, and location-based types, while highlighting challenges like node deployment and energy consumption. It explores specific protocols such as LEACH, a hierarchical model that optimizes energy load and cluster formations, and Rumor Routing, a flat protocol aimed at efficient data transmission through random paths. Design issues include fault tolerance, data aggregation, and quality of service, along with strategies for managing data routing in various scenarios.