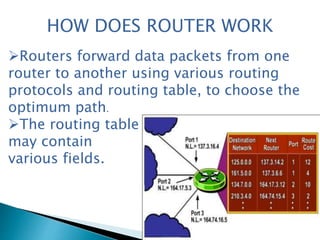
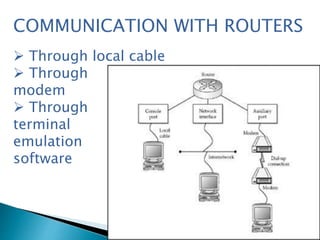
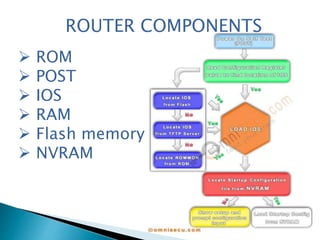
This document discusses router forensics and security. It provides an overview of routers and common router attacks. It outlines the process of performing router forensics, including collecting volatile data, investigating incidents, and documenting findings. The document also discusses why router resources need protection and why router forensics is important for addressing security issues, monitoring activity, and regulatory compliance.