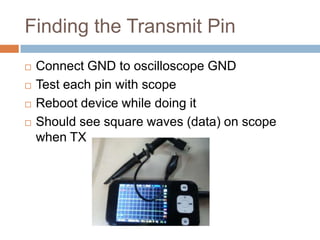
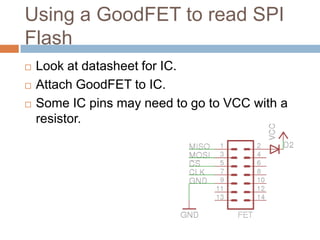
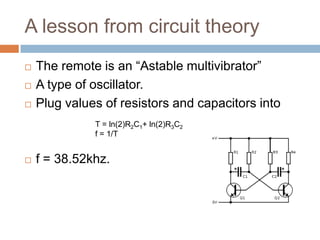
This document provides an introduction to hardware hacking for software engineers. It outlines several beginner hardware hacking projects, including interfacing with UART to gain serial console access on devices, ripping firmware from chips to analyze code and find passwords/strings, manipulating IR alarm systems by learning codes and repurposing remotes, and building an Arduino-controlled backyard irrigation system networked to a PC. The document explains how to identify important chips, interfaces, and voltages, and techniques for reading serial flash and desoldering chips to extract firmware. It presents hardware hacking as an accessible new hobby that can build skills in electronics and low-level programming.