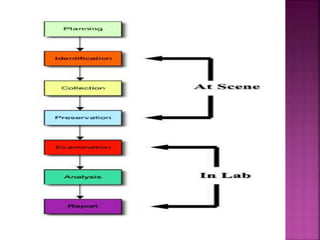
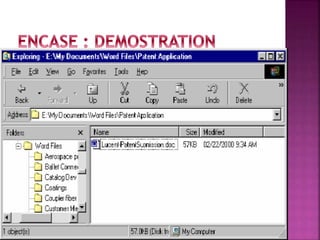
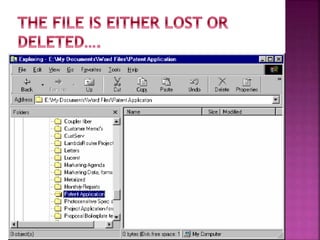
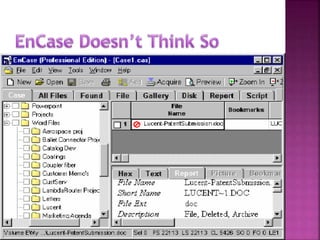
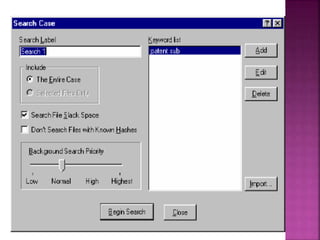
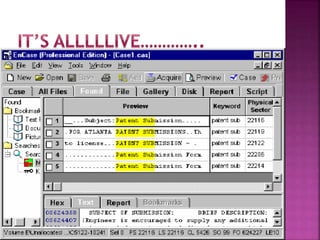
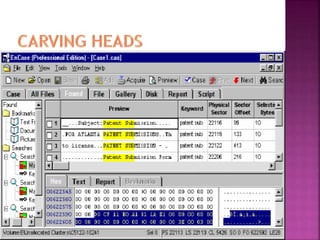
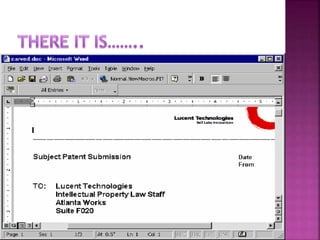
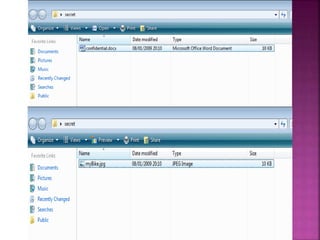
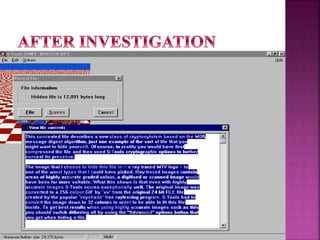
The document discusses the field of computer forensics, which involves the identification, preservation, analysis, and presentation of digital evidence in a legally acceptable manner, particularly in response to increasing cybercrime. It covers various categories of computer forensics, methodologies for evidence collection, handling of volatile and persistent data, and the importance of creating forensic images for legal proceedings. The document also outlines tools and techniques used in forensic investigations, the challenges of managing digital evidence, and the ethical considerations surrounding the practice.