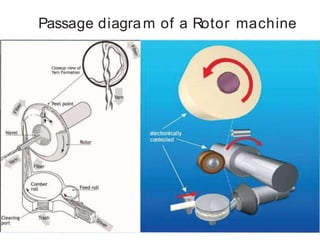
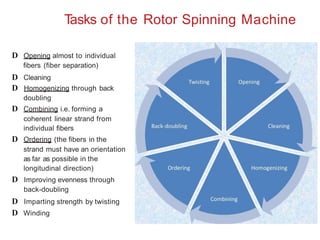
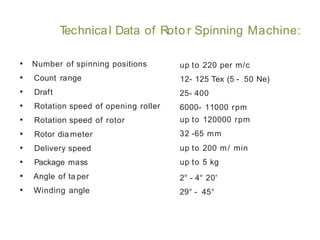
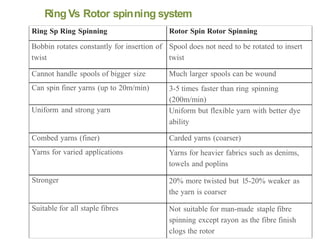
This document summarizes the key differences between ring spinning and rotor spinning systems. Rotor spinning is a more recent open-end spinning method that introduces twist without requiring package rotation. It has higher productivity and handles larger packages than ring spinning. While rotor yarn is weaker, it has better evenness and abrasion resistance. The document provides details on the rotor spinning process and machine parts and compares performance characteristics of ring and rotor yarns.









![Comparison between Ring and Rotor yarn [20 Ne]
Note: This experimenta l data is an average test result out of 8-10 tests. The tests were
done at The Delta Spinning mills Ltd.
Parameters Ring yarn {Card) Rotor yarn
Tenacity (cN/Tex) 17.5 15.1
CSP 2550 1830
Elongation % 3.75 4.35
TPI 14.23 18.31
Uster U% 9.774 9.41
CVm% [ cm] 12.412 11.872
CVm% [3m] 2.882 2.91
Thin [-40%]/Km 20.687 36.56
Thick [+35%] 446.25 178.75
Thick [+50%] 48.125 5
Neps [+200%] 60.3125 26.25
Hairiness Index [H] 7.21 4.65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotorspinning-191227160928/85/Rotor-spinning-17-320.jpg)


