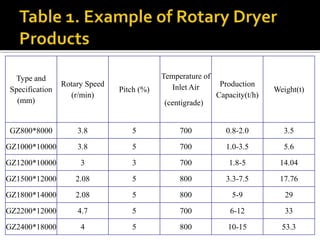
The rotary dryer is a type of industrial dryer that reduces the moisture content of materials by bringing them into direct contact with heated gas. It consists of a cylindrical shell that rotates, allowing material to be fed in at one end and discharged at the lower end as it dries. As the dryer rotates, internal fins lift the material through a hot gas stream to evaporate moisture before it falls back to the bottom. Rotary dryers can dry a wide range of materials effectively and are commonly used in mineral processing to dry products like sands, limestone, ores, and coal.