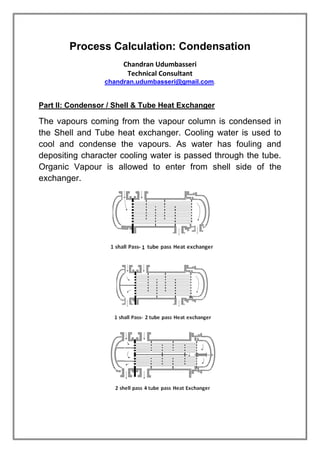
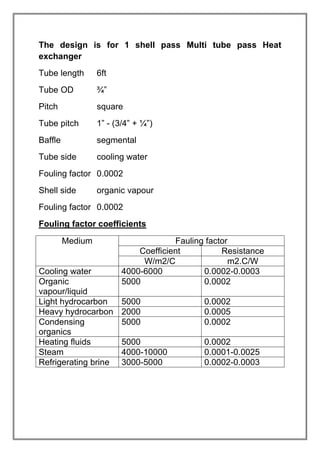
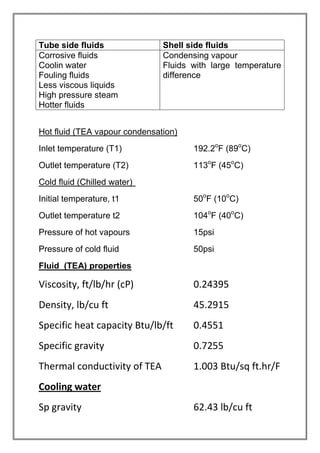
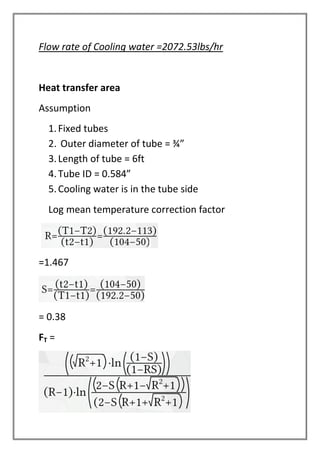
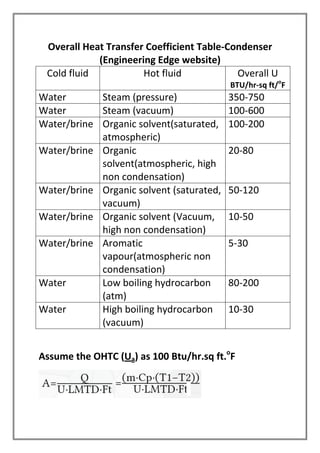
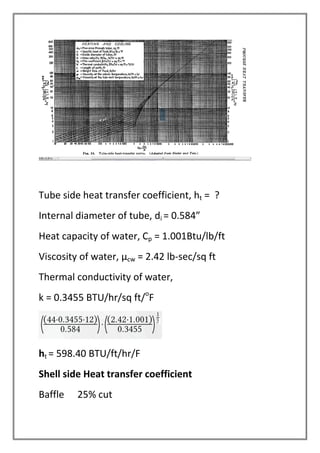
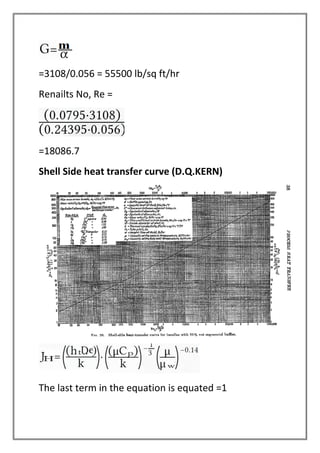
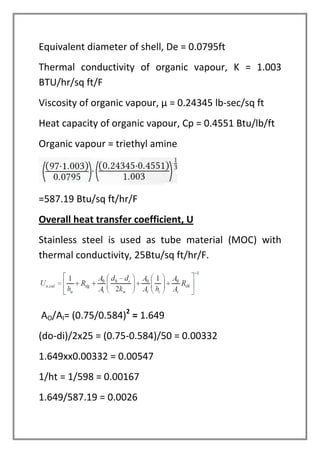
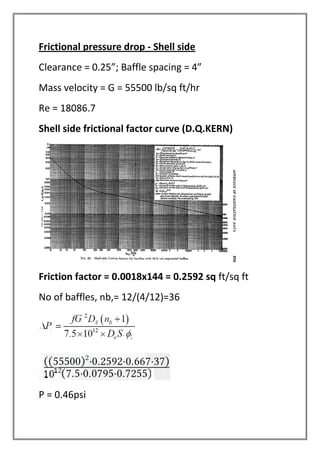
The vapors from a vapor column are condensed in a shell and tube heat exchanger using cooling water. The design is for a multi-tube pass, single shell pass heat exchanger with 8 tubes of 3/4" diameter and 6' length. Energy and heat transfer calculations are shown to determine the required cooling water flow rate of 2072.53 lbs/hr and heat transfer area of 19.86 sqft to achieve the necessary heat transfer. Pressure drops are also calculated to be within acceptable limits.