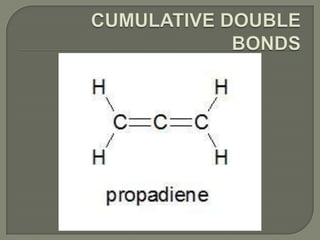
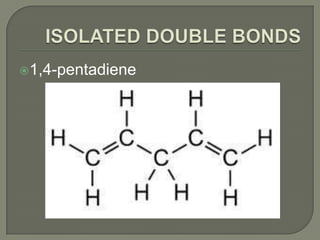
Alkadienes are hydrocarbons that contain two carbon-carbon double bonds. They can be classified based on the location and relationship of the double bonds as cumulated, conjugated, or isolated. Cumulated dienes are reactive, while conjugated dienes have similar physical and chemical properties to alkenes. Isolated dienes behave similarly to monoolefins. Alkadienes are used in the production of tires and plastics. Exposure safety hazards include possible cancer risks from inhalation or skin contact. Symptoms from inhalation include respiratory irritation and effects on the central nervous system. Skin or eye contact may cause burns or irritation.