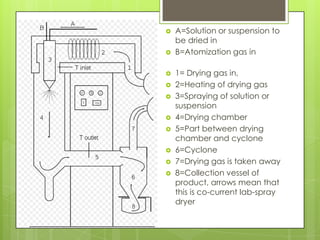
This document discusses different types of dryers and drying processes. It describes spray dryers, oven dryers, freeze dryers, vacuum dryers, rotary dryers, and drum dryers. For each type of dryer it provides a definition, describes the drying process, and lists some common applications. The key information provided includes how each dryer works by removing moisture from materials using methods like applying heat, reducing pressure, or rotating materials to facilitate drying.