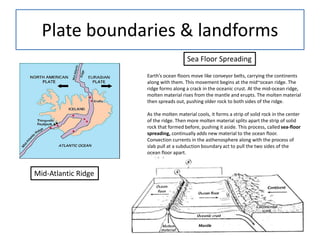
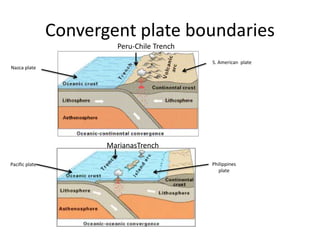
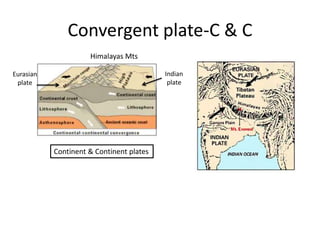
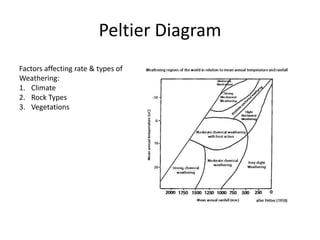
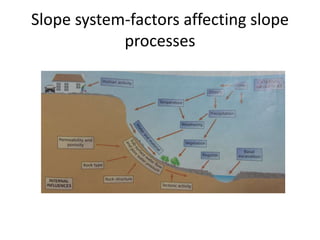
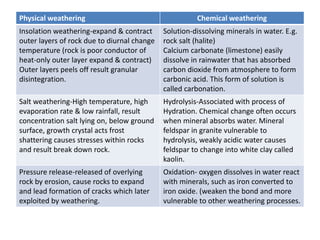
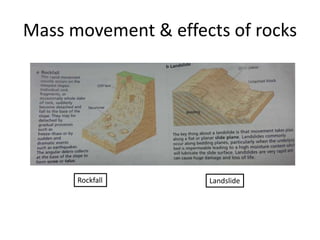
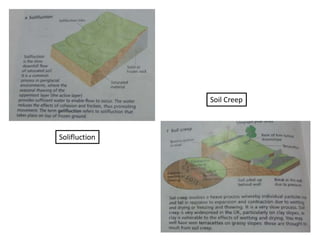
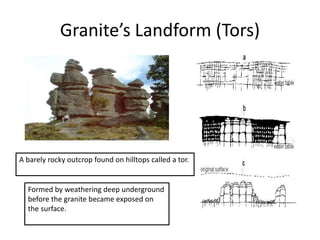
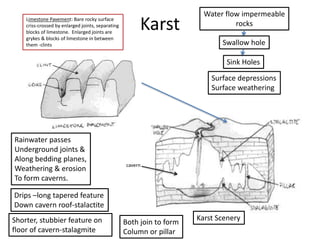
This document summarizes key concepts about plate tectonics and weathering processes. It discusses how molten material rises at mid-ocean ridges, pushing older rock to the sides and forming new ocean floor through sea floor spreading. It also describes factors that influence the rate and type of weathering like climate, rock type, and vegetation. Weathering breaks down rock through physical or chemical processes. Slopes are influenced by many factors and can be stabilized through techniques like planting vegetation or improving drainage.