Embed presentation
Download to read offline

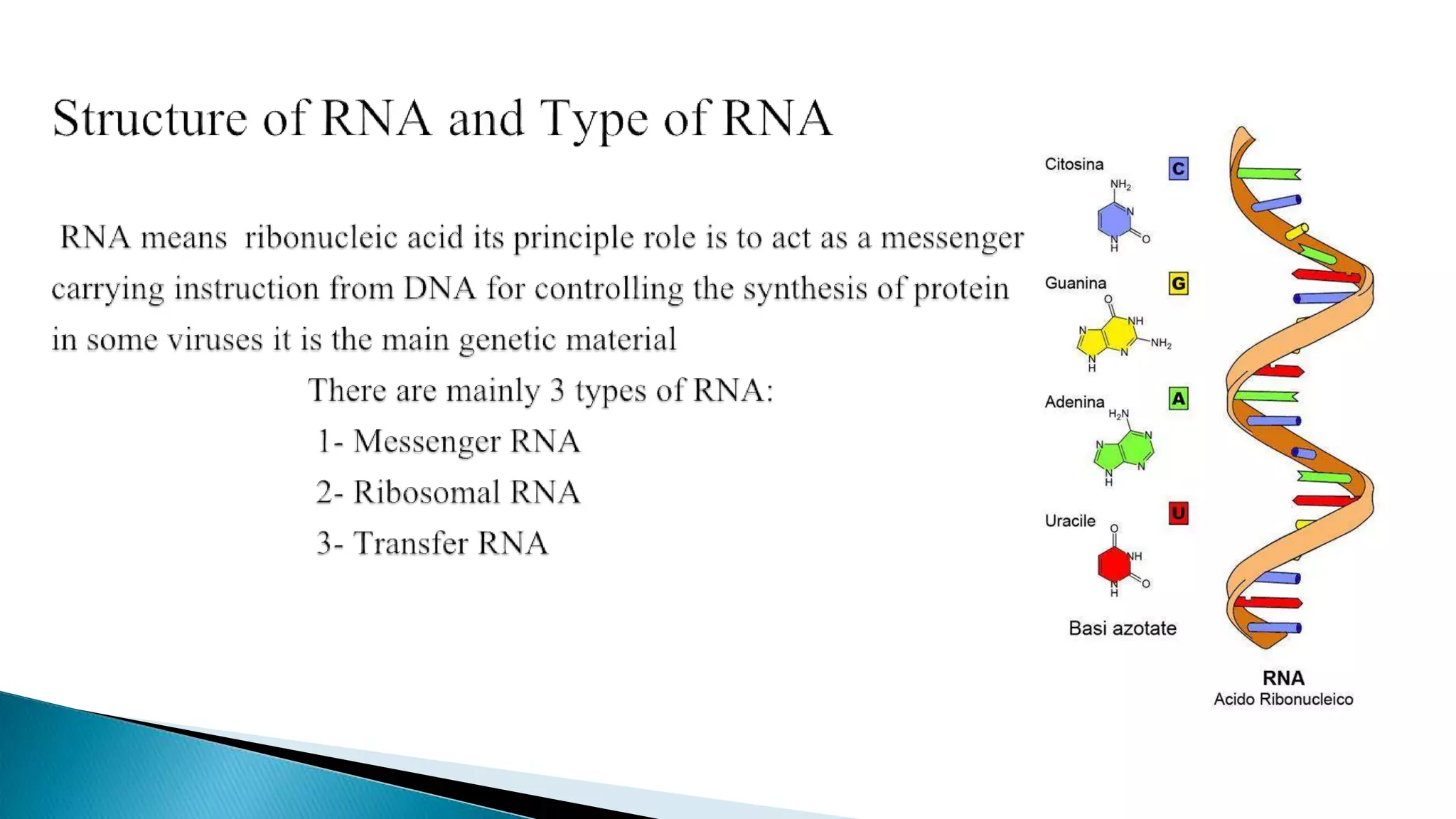
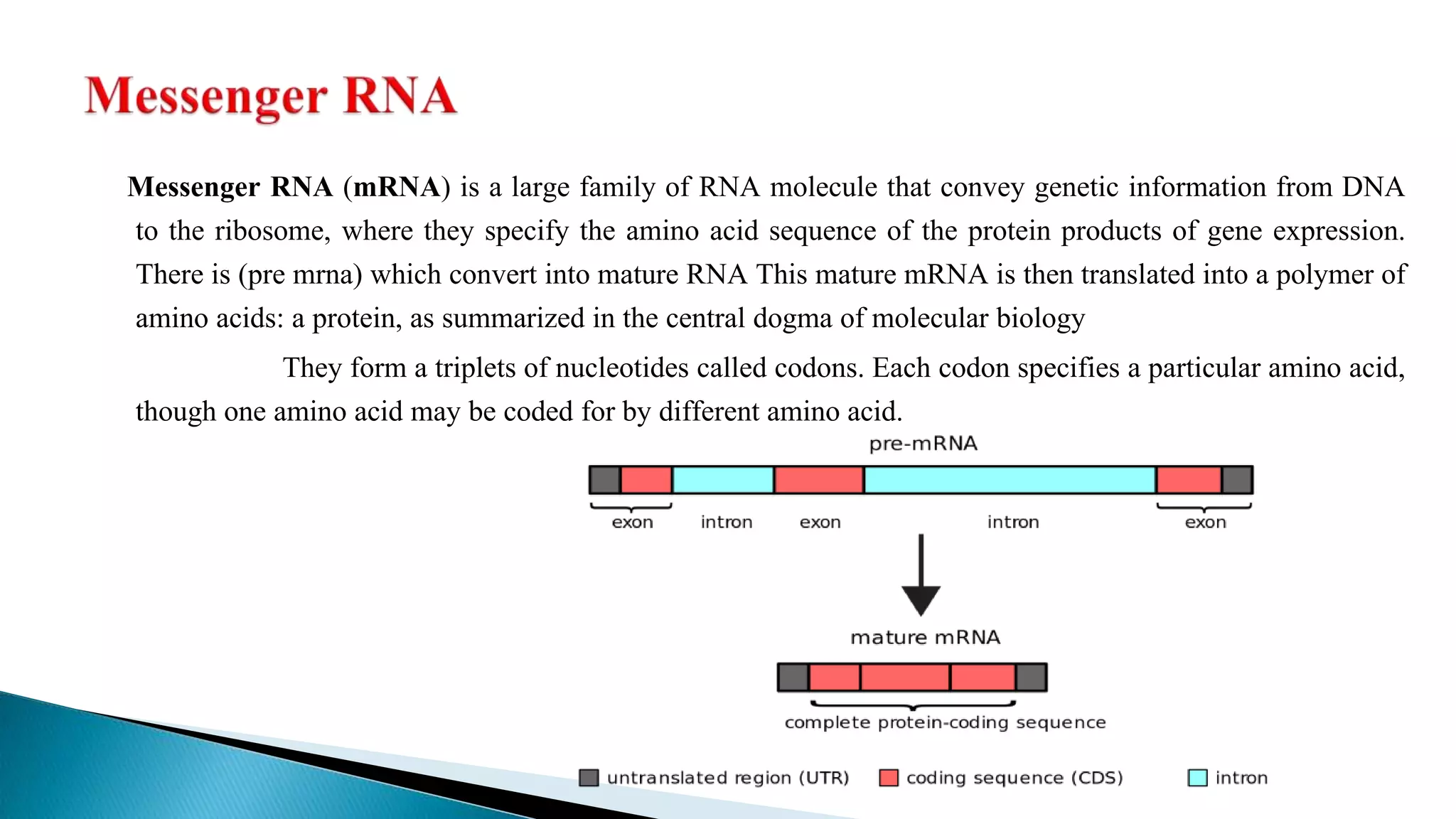

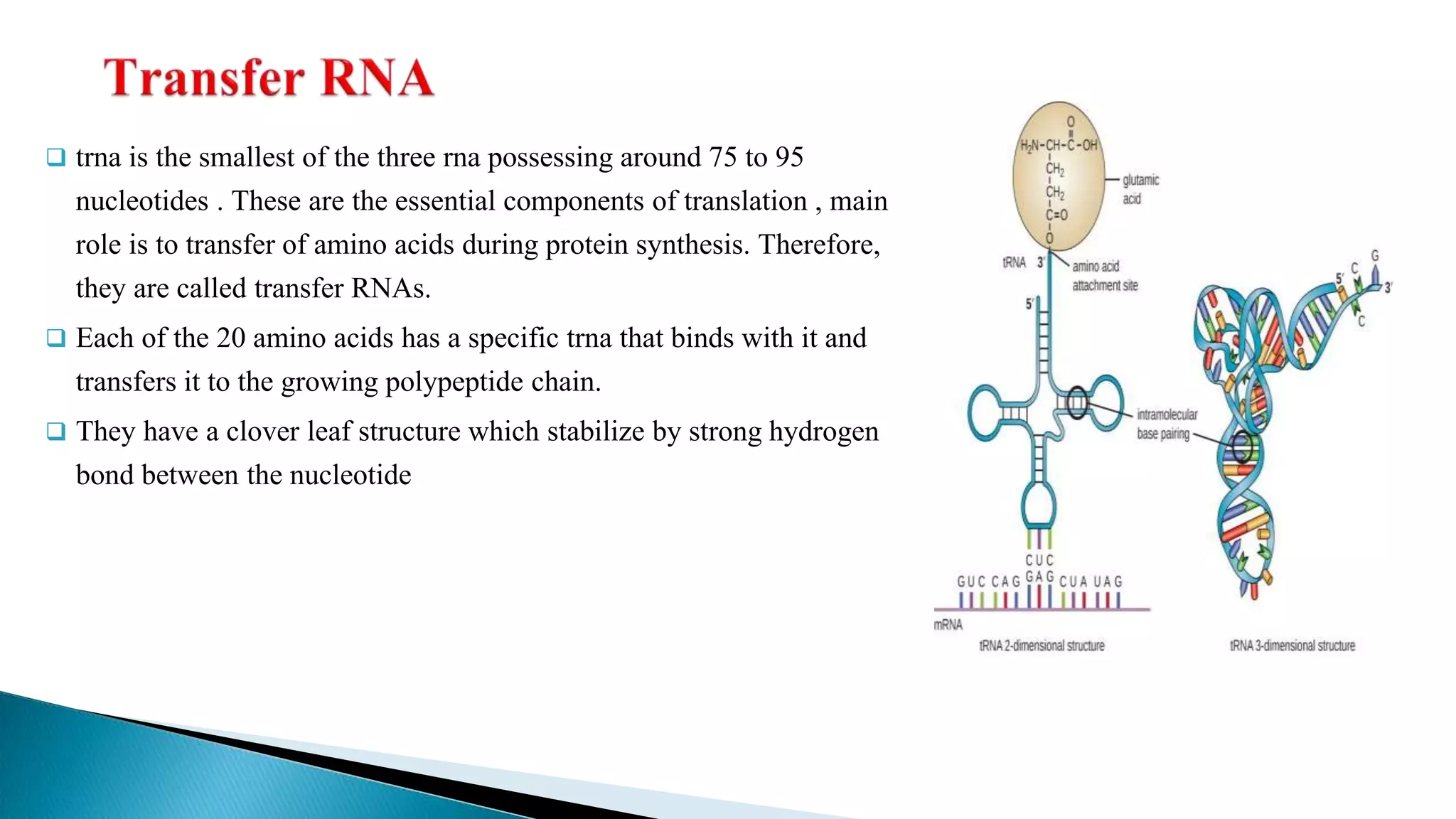
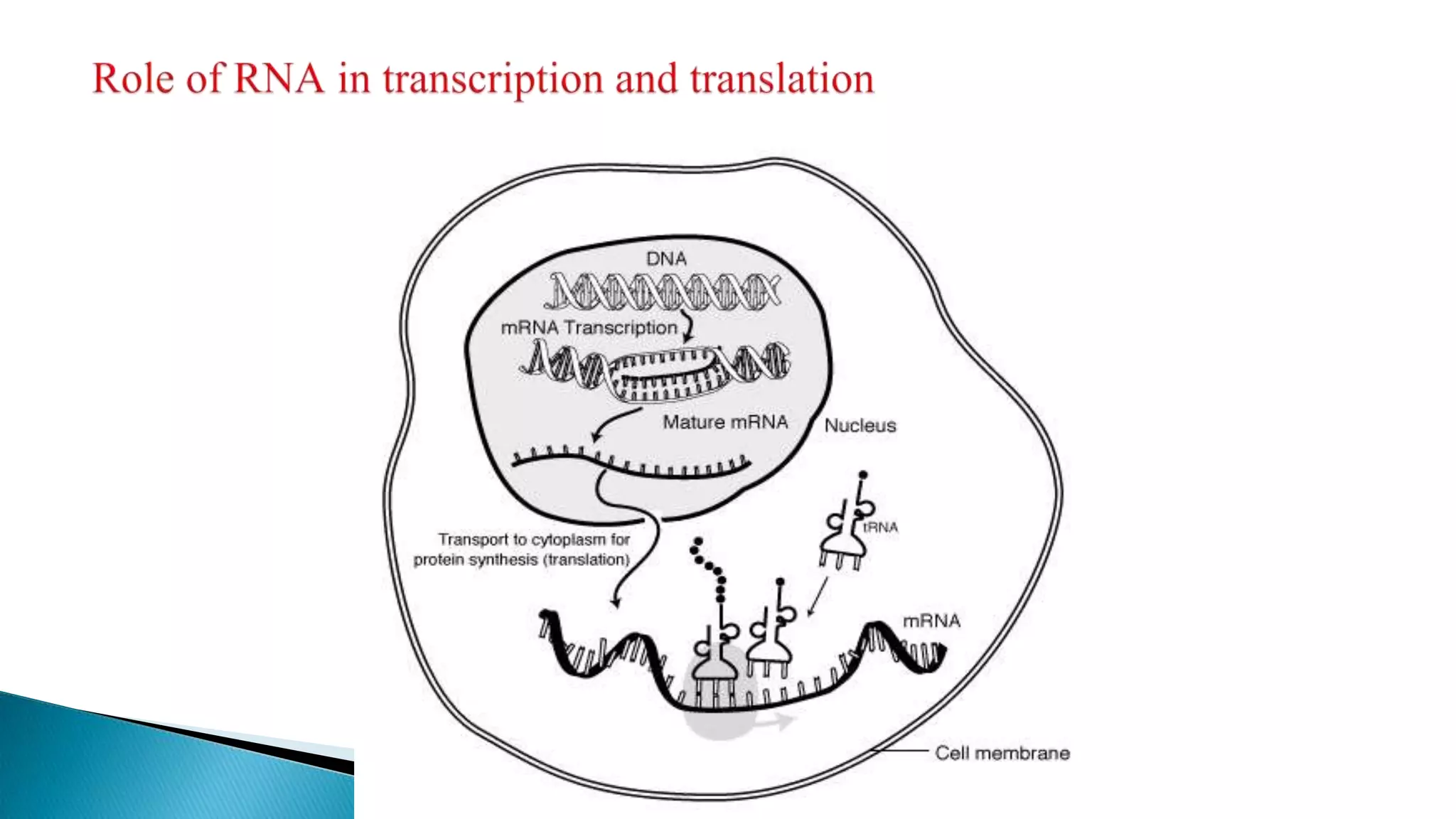


mRNA conveys genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it specifies the amino acid sequence of proteins. mRNA is first transcribed from pre-mRNA and then translated into a polymer of amino acids at the ribosome according to the genetic code stored in codons of three nucleotides each. Ribosomes, composed of rRNA and proteins, move along mRNA during translation and assemble the growing polypeptide chain specified by the mRNA.






