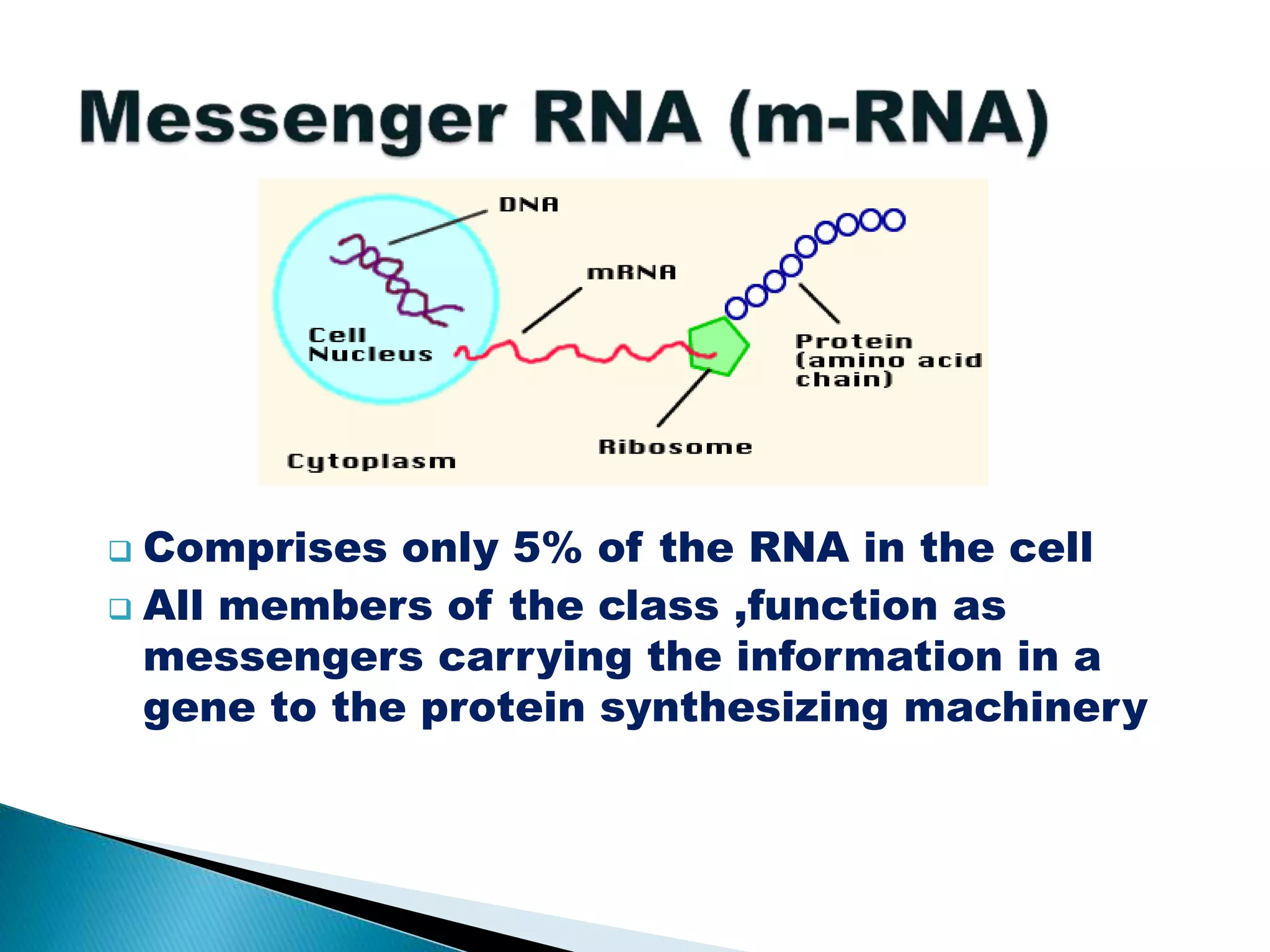
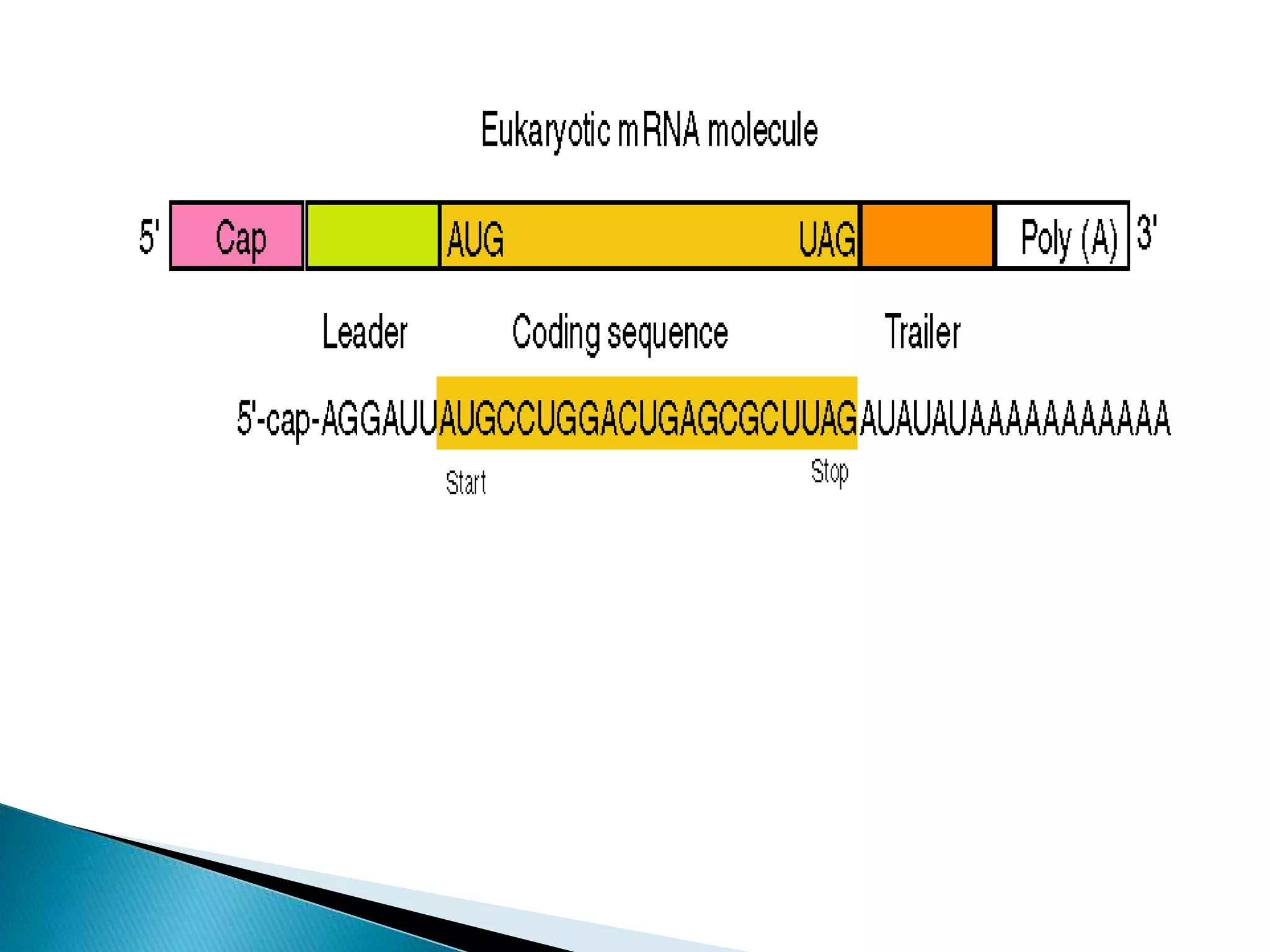
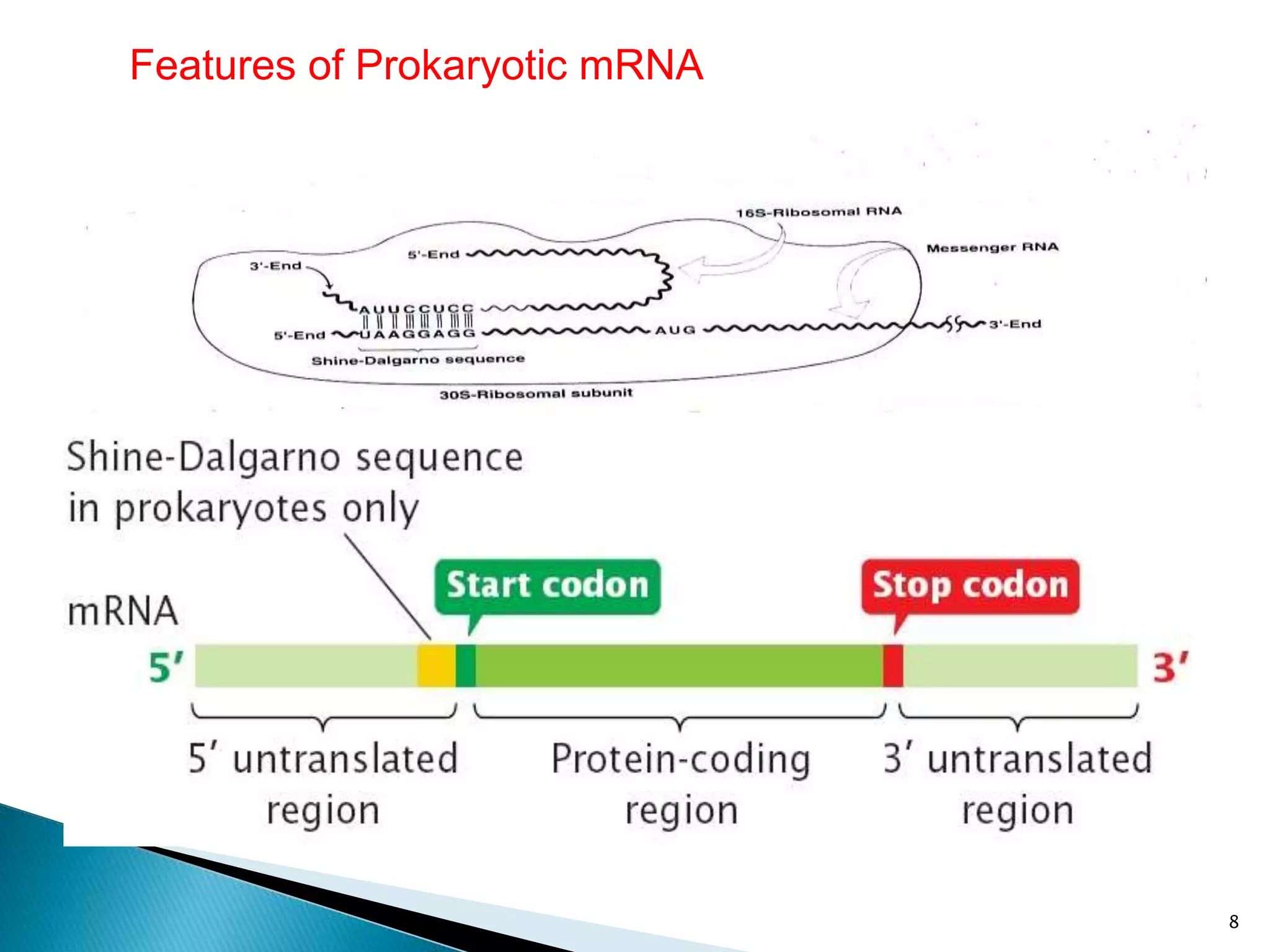
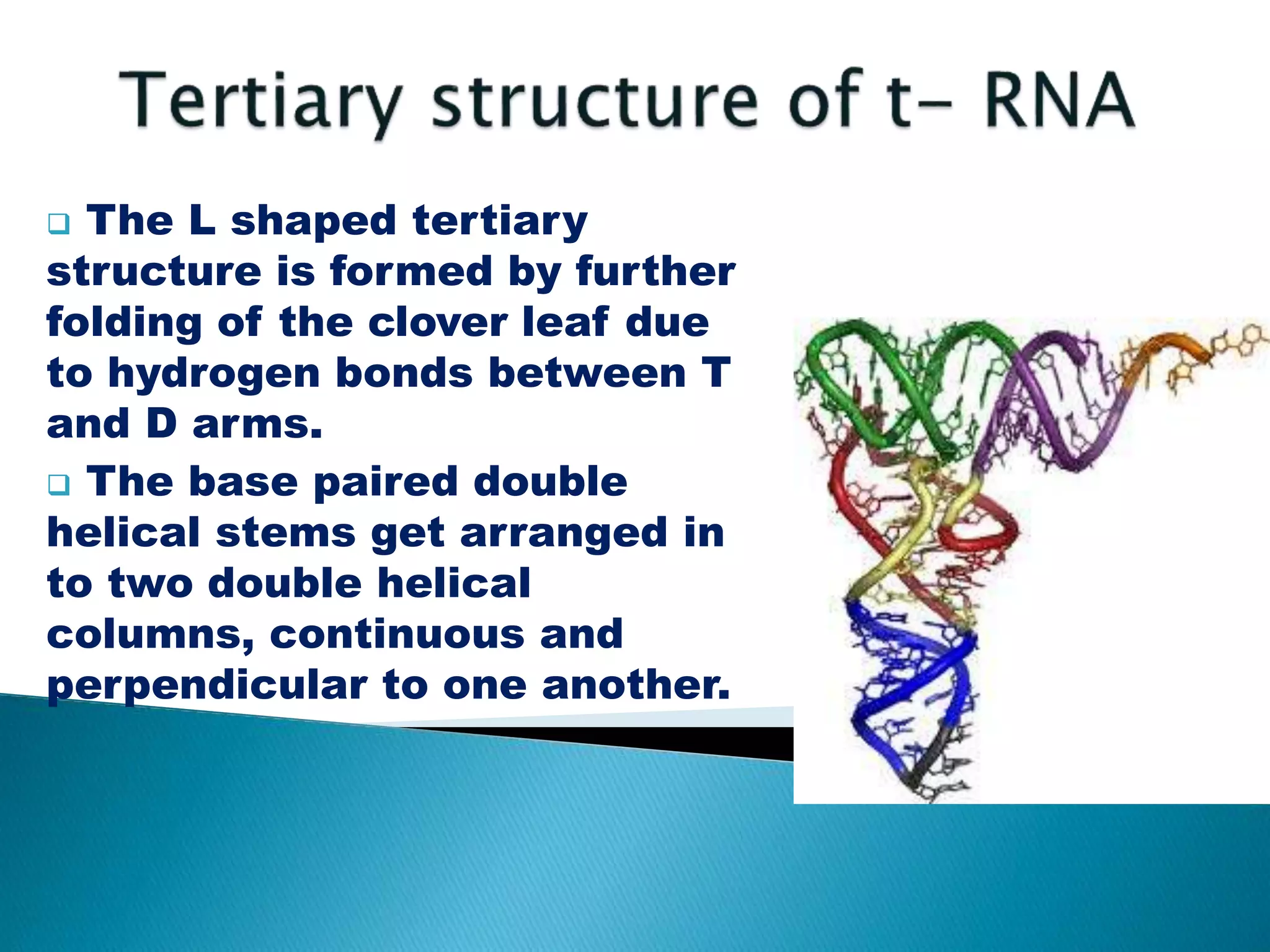
There are three main classes of RNA in organisms: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA comprises 5% of cellular RNA and carries genetic information from genes to the protein synthesis machinery. mRNA has a 5' cap and 3' poly-A tail that aid in its stability and recognition during translation. tRNA transfers amino acids during protein synthesis and has a distinctive cloverleaf secondary structure. rRNA makes up the ribosomal subunits and is necessary for ribosome assembly and translation functions like mRNA binding and peptidyl transferase activity.