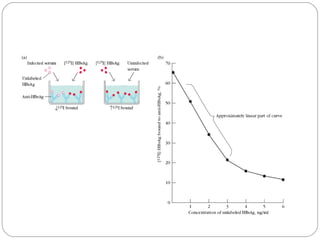
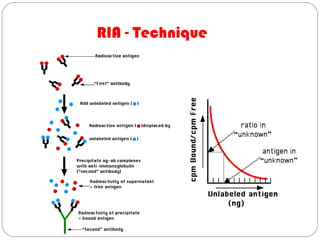
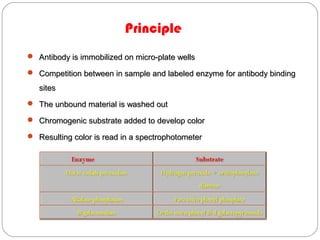
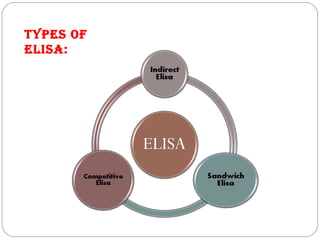
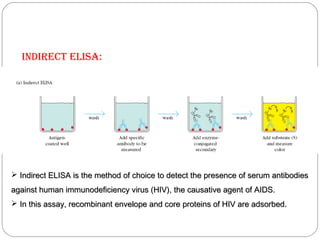
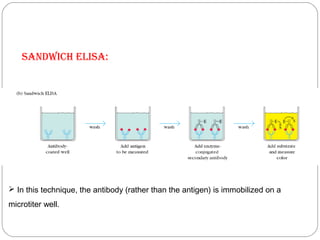
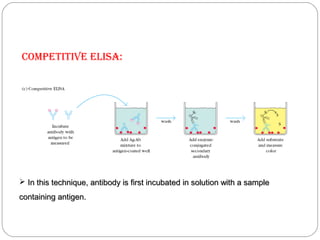
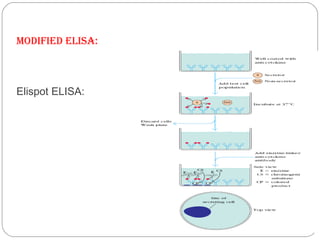
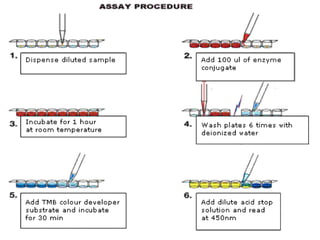
Immunoassays such as radioimmunoassay (RIA) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are biochemical tests that use antibodies to detect and measure substances like drugs, hormones, proteins, and tumor markers in biological samples. RIA uses radioactive isotopes to detect antigens or antibodies and is highly sensitive, while ELISA uses an enzyme-linked antibody to detect the presence of an antigen or antibody without radioactivity. Both tests are useful for clinical applications like detecting endocrine disorders, drug abuse, allergies, and cancer.