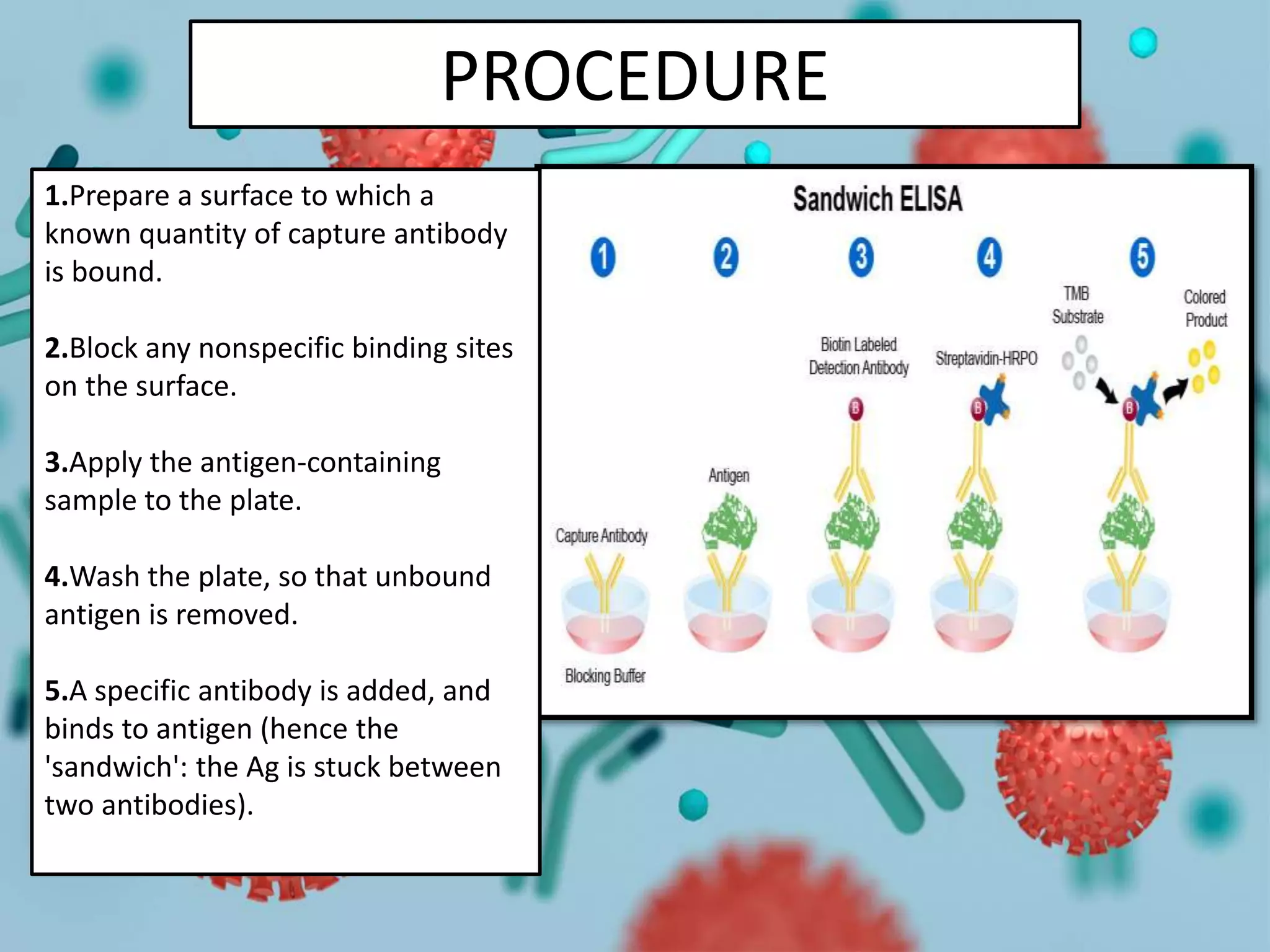
Sandwich ELISA is a highly efficient method for detecting antigens using two layers of antibodies, requiring that the target antigen has at least two distinct epitopes. The procedure involves coating a plate with a capture antibody, adding the antigen sample, and then detecting the bound antigen with an enzyme-linked secondary antibody, which produces a measurable signal. While it offers advantages such as high sensitivity, specificity, and suitability for complex samples, optimizing antibodies can be challenging.