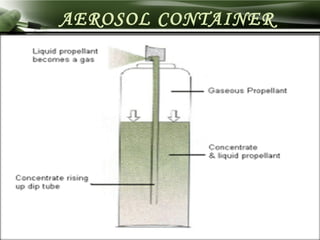
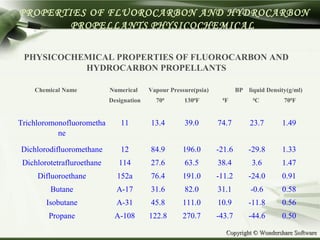
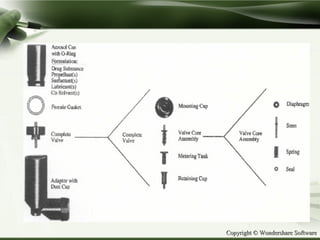
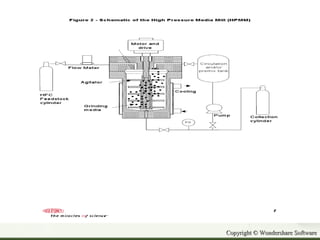
The document discusses advances in propellants for aerosol drug delivery. It provides a history of aerosol development beginning in the 1950s. Traditionally, most pharmaceutical aerosols used chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) as propellants but these deplete the ozone layer. Current alternatives being used are hydrofluorocarbons such as HFA-134a and HFA-227ea which have acceptable toxicity profiles. The document discusses the components of aerosols including propellants, containers, valves and actuators. It defines propellants and their role in aerosols, and provides examples such as compressed gases like carbon dioxide and liquefied gases including hydrocarbons and hydrofluoroalkanes.