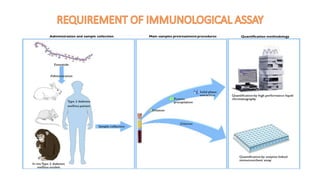
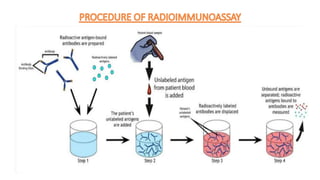
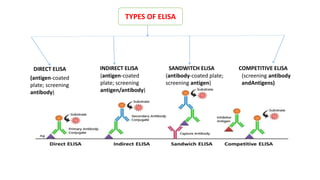
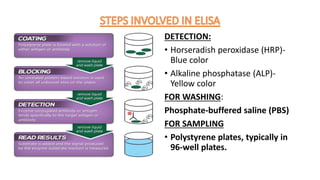
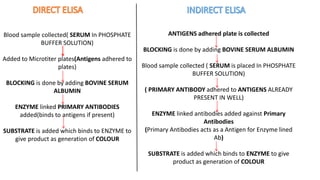
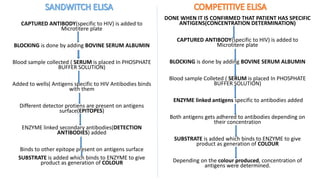
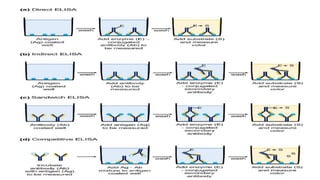
This document summarizes Radioimmunoassay (RIA) and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) techniques. RIA was developed in 1959 and uses radioactive molecules to detect antigens or antibodies in biological samples. It is highly sensitive but requires special safety precautions due to radioactivity. ELISA was developed later and uses enzyme-linked antibodies to detect antigens or antibodies through a color change reaction. It has advantages over RIA like no radioactivity, higher sample throughput, and easier automation. Both techniques are widely used in clinical diagnostics, research, and other applications to detect various molecules.









![• Aydin S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our
laboratory experience with peptide/protein analyses using ELISA.
Peptides. 2015 Oct;72:4-15. [PubMed]
• Weng X, Gaur G, Neethirajan S. Rapid Detection of Food Allergens by
Microfluidics ELISA-Based Optical Sensor. Biosensors (Basel). 2016 Jun
07;6(2):24. [PMC free article]
• Journals of Immunoassaand Immunochemistry 25(3) 241-258
• www.google.comimages
• www.slideshare.Net](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immunologicalassays-230326065332-1bf8def1/85/IMMUNOLOGICAL-ASSAYS-pptx-17-320.jpg)
