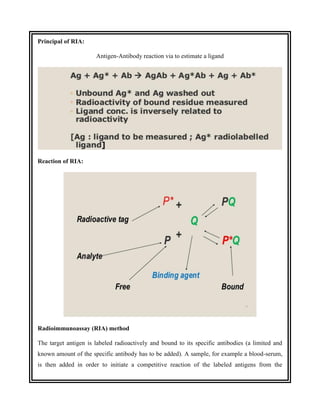
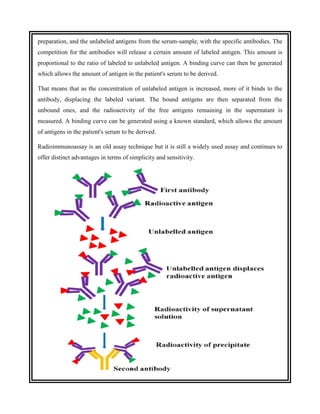
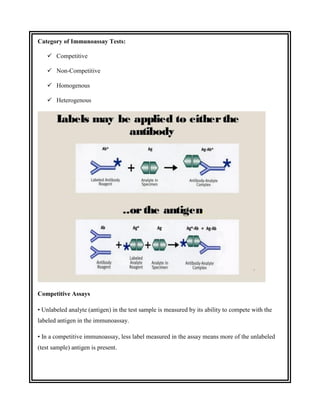
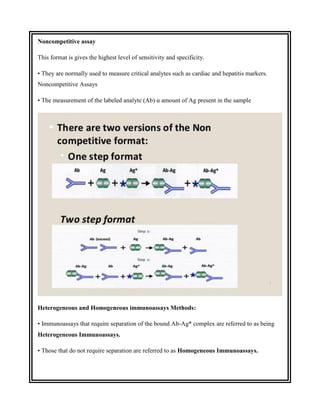
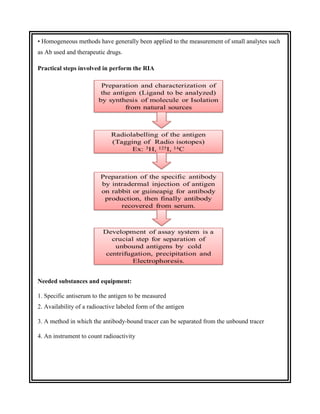
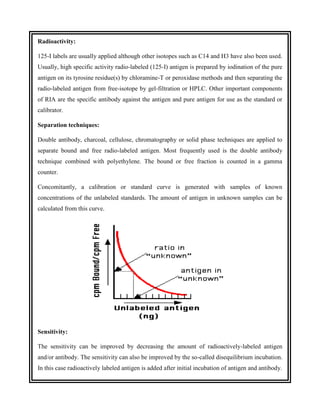
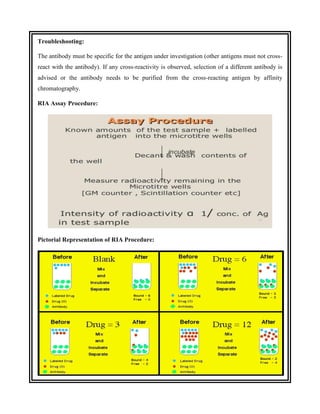
This document discusses the history and development of radioimmunoassay (RIA) by Rosalyn Yalow, who won the Nobel Prize for her work. RIA involves labeling an antigen with a radioactive isotope, then using the specificity of the antibody-antigen reaction to separate bound labeled antigen from unbound antigen. This allows for quantification of antigens even at very low concentrations. The document outlines the principles, procedures, applications, advantages and disadvantages of RIA.