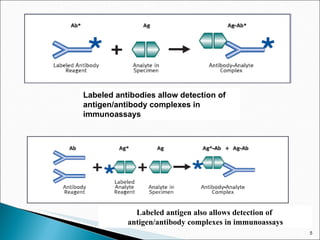
The document discusses radioimmunoassay (RIA), a laboratory technique that uses the principle of competitive binding between labeled and unlabeled antigens or ligands to measure concentrations. RIA uses antibodies to bind antigens or ligands, one of which is radiolabeled. The amount of radiolabeled antigen/ligand bound is inversely proportional to the concentration of unlabeled antigen/ligand in the sample. The document covers principles, methodology, types of immunoassays and their components, and applications of RIA.


![Principle: Uses an immune reaction [Antigen – Antibody reaction] to estimate a ligand Ag + Ag* + Ab AgAb + Ag*Ab + Ag + Ag* Unbound Ag* and Ag washed out Radioactivity of bound residue measured Ligand conc is inversely related to radioactivity [Ag : ligand to be measured ; Ag* radiolabelled ligand]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ria-111010042520-phpapp02/85/RIA-ppt-akshay-patel-3-320.jpg)


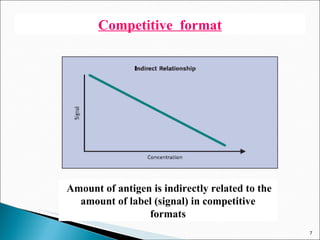
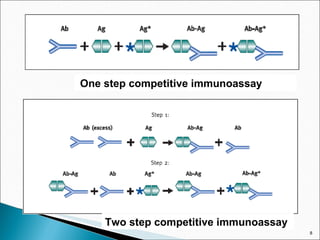
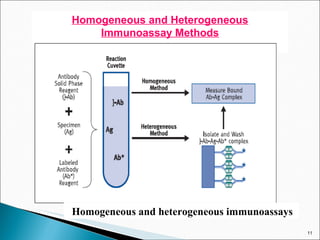
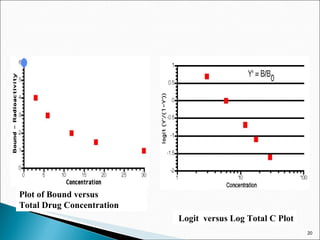
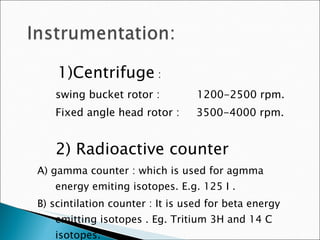
![Limited reagent assay: Many conventional RIAs follow limited reagent assay protocols. The following scheme depicts the AgAb reaction: Ag AgAb + Ab Ag* Ag*Ab With limited amount of Ab, the unlabeled antigen (analyte) competes with the labeled antigen Ag* for limited binding sites. Bound fraction [AgAb] is separated from free [Ab], and the signal [Ag*Ab] complex i.e. the Ab fraction not occupied by the analyte is measured. The amount of analyte is inversely proportional to the bound [Ag*Ab] complex in a hyperbolic function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ria-111010042520-phpapp02/85/RIA-ppt-akshay-patel-12-320.jpg)
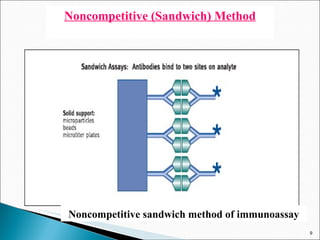
![Excess-Reagent assay This protocol is utilized by- 1. Immunoradiometric Assays (IRMA). 2. Two-site or sandwich Assays. Here the excess Ab is labeled.(In case of sandwich assay an excess amount of first Ab used to capture analyte from sample matrix, and a labeled second Ab provides the signal for quantitation.) IRMA : Ag + Ab* AgAb* Sandwich assay: Ag + Ab1 Ag-Ab1 + Ab2* Ab1-Ag-Ab2* Bound fraction is separated from free; the signal [AgAb*] or [Ag-Ab1-Ab2*] complex is measured. The amount of analyte is proportional to the bound complex in a hyperbolic function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ria-111010042520-phpapp02/85/RIA-ppt-akshay-patel-13-320.jpg)


![Preparation & characterisation of the Antigen [Ligand to be analysed] Radiolabelling of the Antigen Preparation of the Specific Antibody Development of Assay System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ria-111010042520-phpapp02/85/RIA-ppt-akshay-patel-16-320.jpg)
![Antigens prepared by.. Synthesis of the molecule Isolation from natural sources Radiolabelling [Tagging procedure] 3 H 14 C 125 I are used as radioactive tags Antigens are tagged to 3 H 14 C 125 Tagging should NOT affect Antigenic specificity & Antigenic activity !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ria-111010042520-phpapp02/85/RIA-ppt-akshay-patel-17-320.jpg)

![Add known amounts of the test sample + labelled antigen into the microtitre wells Incubate allow the reaction to reach completion Decant & wash contents of the well removes all unbound antigens Radioactivity remaining in the Microtitre wells measured by a Counter [GM counter , Scintillation counter etc] Intensity of radioactivity is inversely correlated with the conc of antigens in the test sample Sensitive to very low conc of antigens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ria-111010042520-phpapp02/85/RIA-ppt-akshay-patel-19-320.jpg)