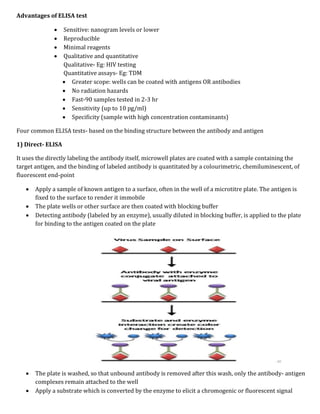
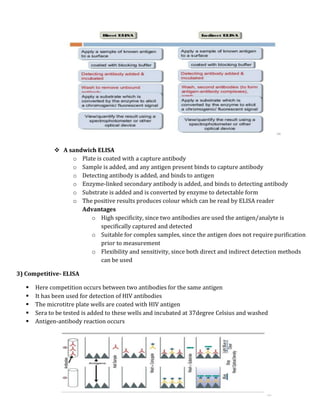
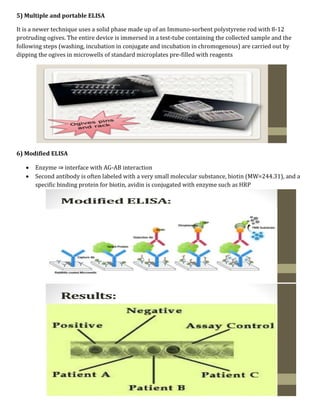
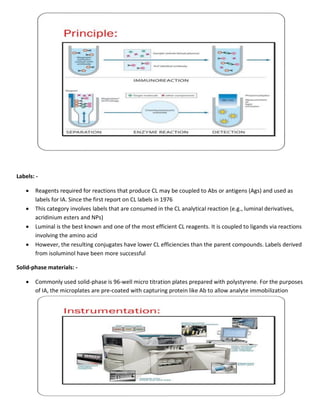
Immunological assays use antibodies or antigens to detect the presence or concentration of a molecule in a solution. There are several types of immunoassays including radioimmunoassays (RIA), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), and bioluminescence assays. RIA uses radioactive labels on antigens or antibodies for highly sensitive detection, but requires special safety precautions. ELISA is a common plate-based assay that uses enzyme labels for detection and has advantages like sensitivity, reproducibility, and flexibility. Bioluminescence assays convert chemical energy from reactions involving luciferins, luciferases, and oxygen into detectable light for applications like cell proliferation analysis.