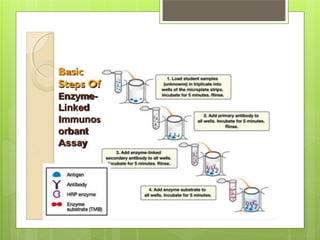
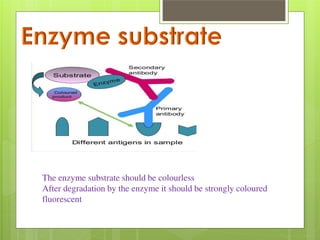
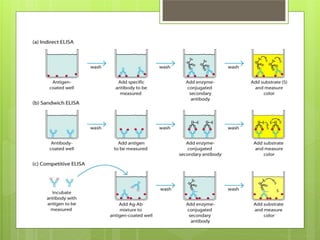
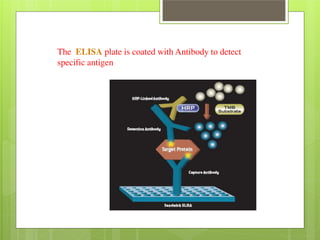
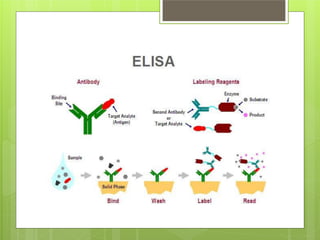
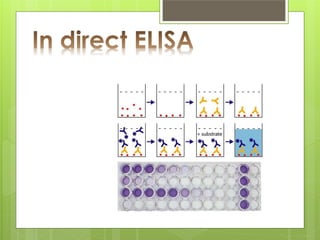
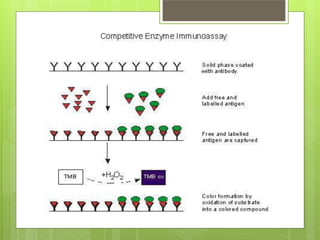
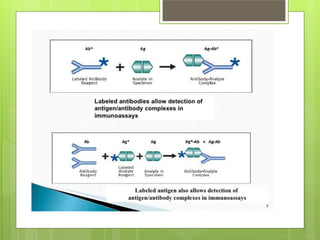
This document provides an overview of two immunoassay techniques: ELISA and RIA. ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) detects the presence of an antigen or antibody using an enzyme-linked secondary antibody that produces a colored product when reacted with a substrate. RIA (radioimmunoassay) uses a radiolabeled antigen or antibody to compete with unlabeled antigens in a sample, and measures radioactivity to determine antigen concentration. Both techniques rely on the specificity of the antigen-antibody reaction and can be used to detect various targets like hormones, drugs, and infectious diseases.

























![Unbound Ag* and Ag washed
Radioactivity of bound residue measured
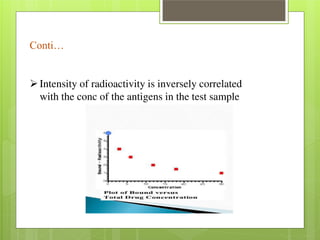
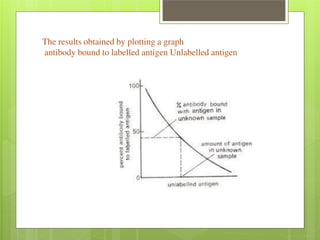
Ligand conc is inversely related to radioactivity
[Ag: ligand to be measured ;Ag* radiolabelled ligand ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elisaria-140928235953-phpapp02/85/Elisa-ria-33-320.jpg)
![Materials required
a) Preparation &characterisation of Antigen [Ligand to be
analysed ]
b) Radiolabelling of the Antigen
c) Preparation of the specific antibody
d) Development of Assay system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elisaria-140928235953-phpapp02/85/Elisa-ria-35-320.jpg)
![PREPARATION AND RADIOLABELLING
OF THE ANTIGEN
Antigens prepared by
synthesis of the molecule isolation from natural sources
Radiolabelling [Tagging procedure ]
3H,14C,125I are used as radioactive tags Antigens are tagged to 3H14c125I tagging should NOT affect antigenic specificity and activity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elisaria-140928235953-phpapp02/85/Elisa-ria-36-320.jpg)

![ASSAY Procedure
Add known amounts of the test sample+ labelled
antigen into the microtitre wells
incubate – allow the reaction to reach completion Decant and wash the contents of the well-removes
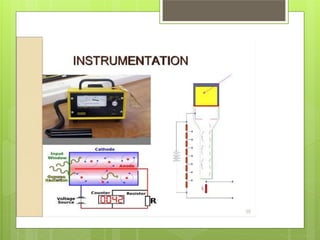
all unbound antigens Radioactivity remaining in the mocrotitre wells
measured by a counter [GM counter, scintillation
counter]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elisaria-140928235953-phpapp02/85/Elisa-ria-38-320.jpg)