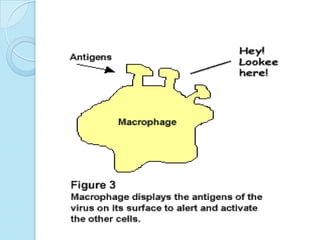
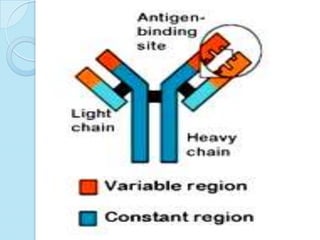
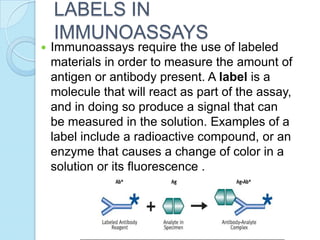
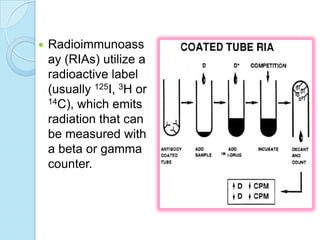
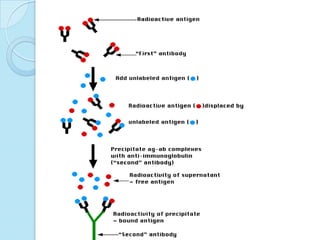
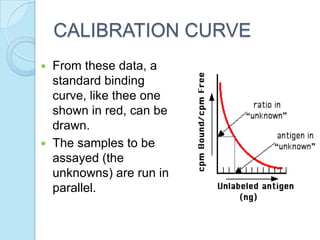
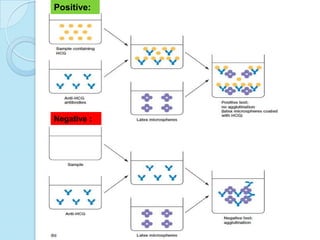
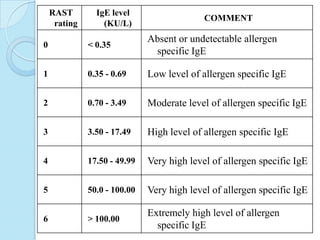
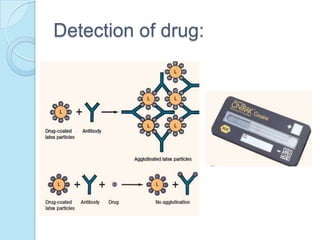
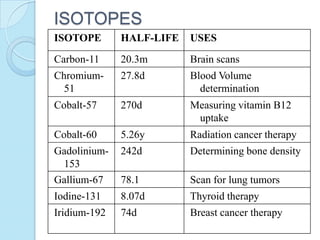
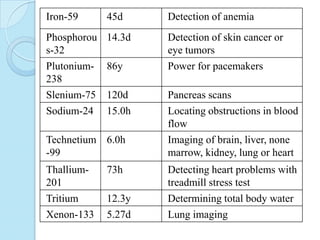
Radioimmunoassay was introduced in 1960 as an assay for measuring insulin levels in plasma. It represented the first invitro technique for detecting hormone levels in blood. The technique uses radioactive labels on antigens or antibodies to allow quantification of antigens or antibodies in a sample by competing them against known standards in binding to antibodies or antigens. It provides a highly sensitive method for detecting hormones, drugs, toxins, and other molecules and has revolutionized research and clinical practice.