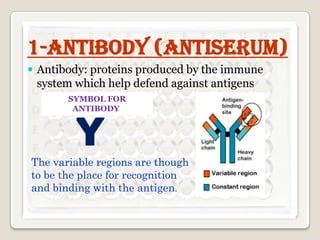
1. ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is an immunoassay technique used to detect antibodies, proteins, peptides, and other molecules. It relies on an antigen-antibody reaction to detect the presence of a substance.
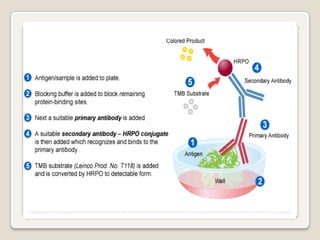
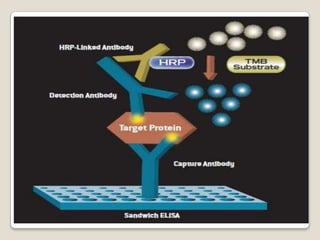
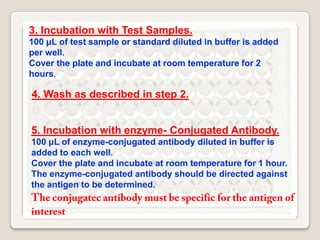
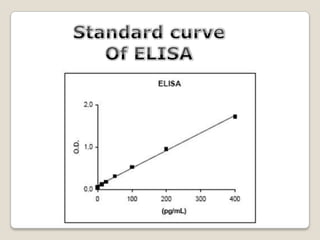
2. The document provides detailed information on the basic principles and steps of ELISA, including coating a plate with antibodies, adding samples and reagents, washing steps, and detecting reactions using enzymes and substrates.
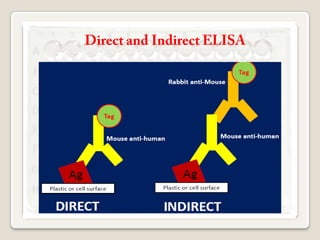
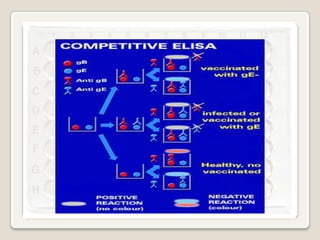
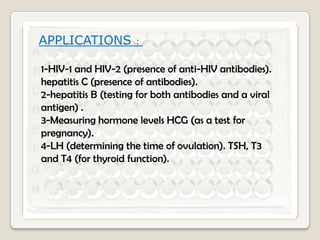
3. Key aspects of performing ELISA are discussed such as sample treatment and storage, controlling humidity and air flow during incubations, and troubleshooting poor results. Direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISA techniques are also summarized.