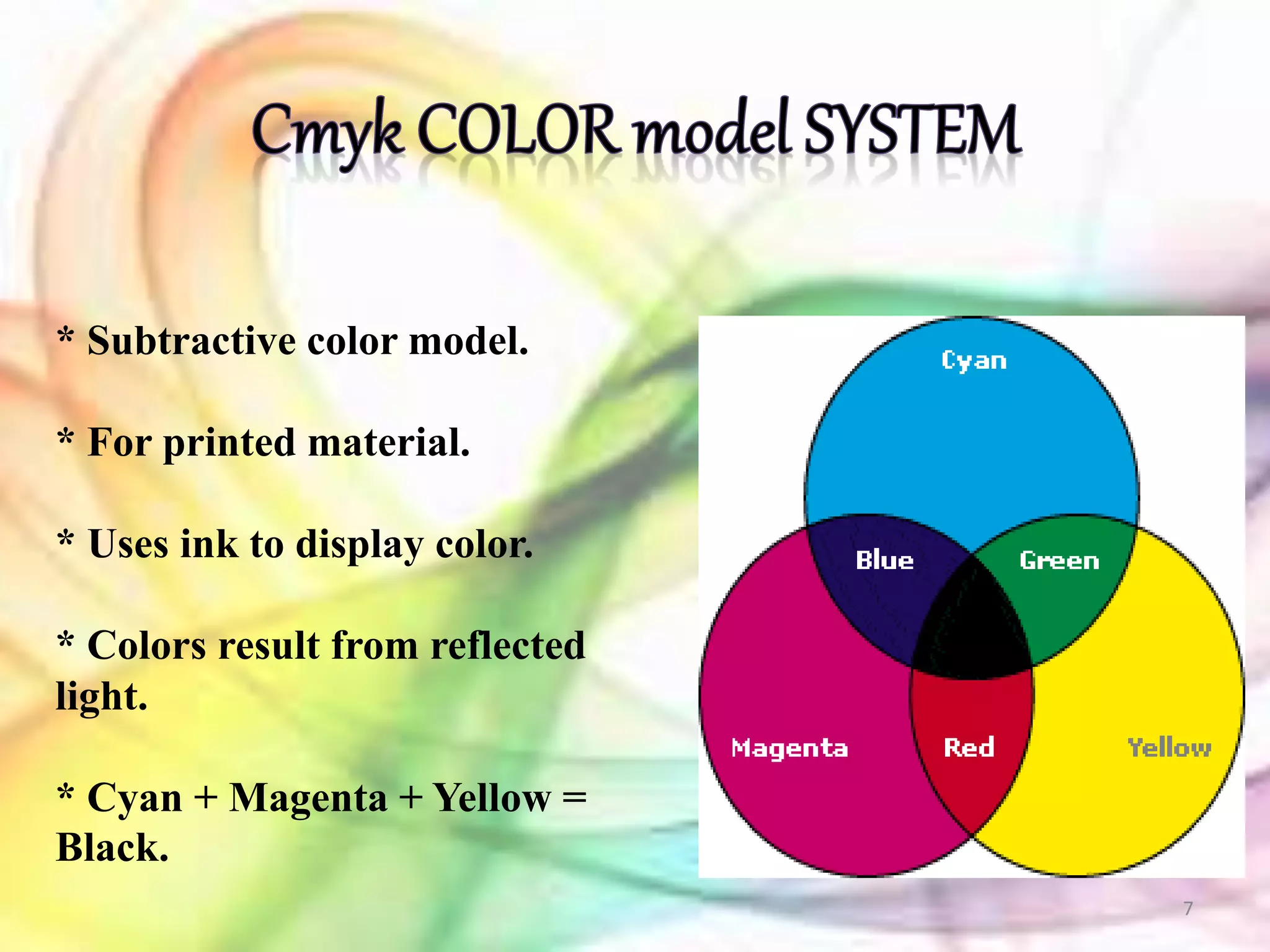
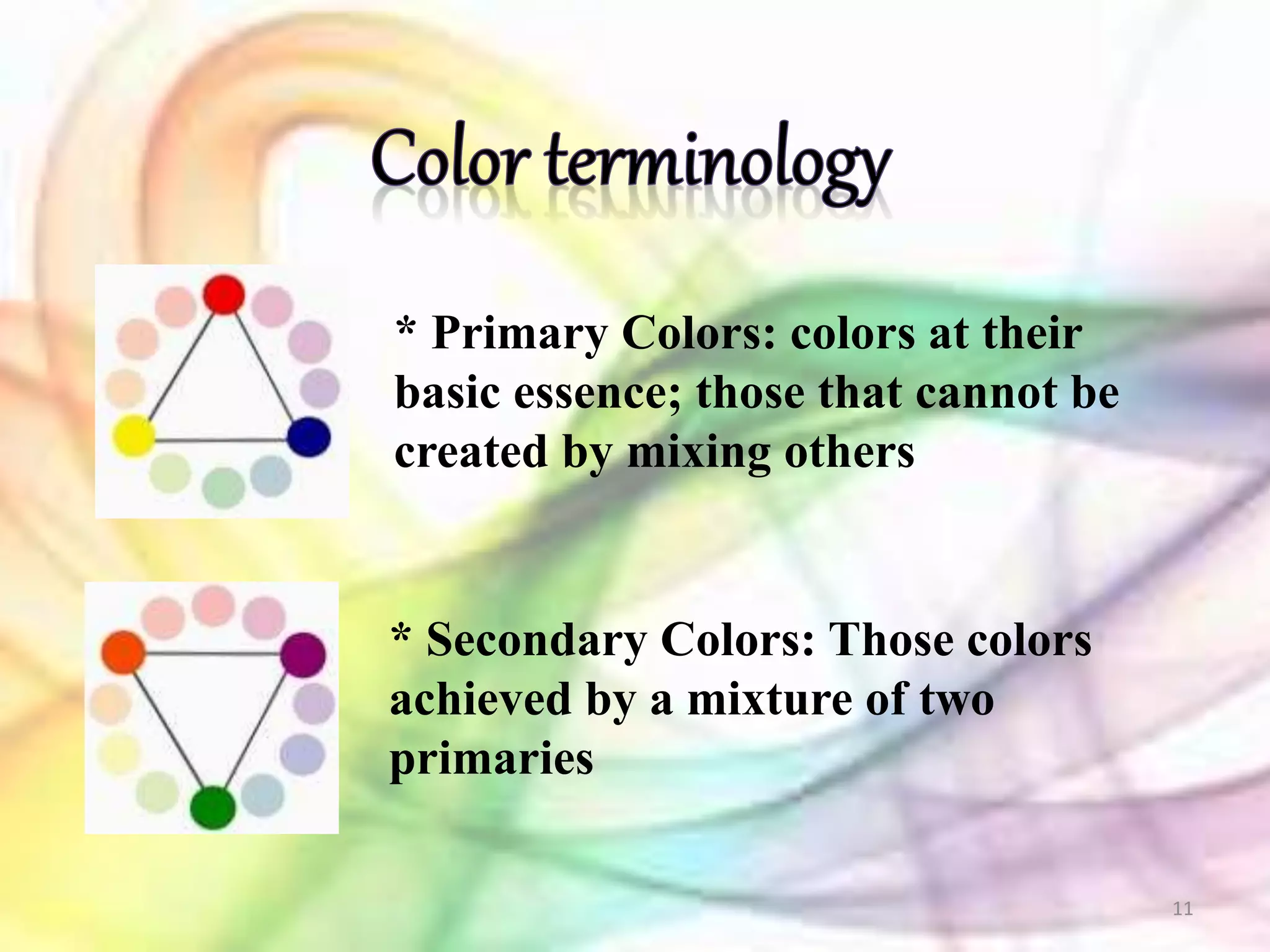
The RGB and CMY color models are two primary systems for representing color digitally. The RGB model uses additive color mixing of red, green, and blue light to reproduce a wide gamut of colors on computer screens. It is well-suited for digital imaging. The CMYK model uses subtractive color mixing of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks to reproduce colors for print. It is widely used in color printing. Both models can be described using numeric values or percentages of their primary colors to precisely define a specific hue.