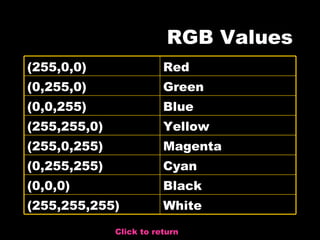
The document discusses color in multimedia applications. It defines color as the visible range of light, which is a continuum from red to violet. It describes how the human eye perceives color through light receptors sensitive to red, green, and blue. It explains color models like RGB, CMYK, and HSB/HSL that are used to represent and display colors digitally using combinations of primary colors.