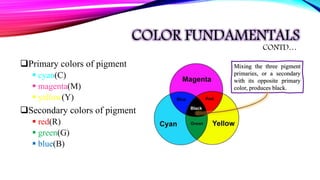
The document discusses color fundamentals, models, and their applications in image processing, detailing how color is perceived and categorized by characteristics such as hue, brightness, and saturation. It explores various color models including RGB, CMY, CMYK, and HSI, explaining their roles in digital representation and practical uses in photography and printing. Additionally, it covers the conversion between these models and the mathematical relationships involved in color processing.









![COLOR MODELS
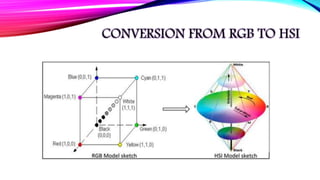
RGB
Each color appears in its primary colors red,
green, and blue
Based on Cartesian coordinate system
All color values R, G and B have been
normalized in the range [0, 1]
We can represent each of R, G and B from 0
to 255
CONTD…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colorfundamentalsandcolormodels-210127171226/85/Color-fundamentals-and-color-models-Digital-Image-Processing-11-320.jpg)










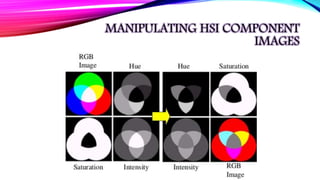
![COLOR MODELS
CONTD…
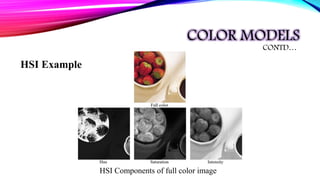
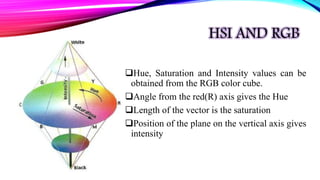
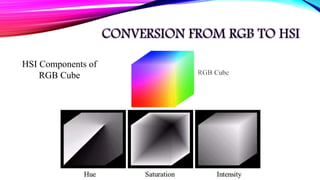
HUE SATURATION INTENSITY
Component that
describes a pure color
(pure yellow, orange or
red)
Component represents the
measure of the degree to
which color is mixed with
white color.
0 degree – Red
120 degree – Green
240 degree – Blue
60 degree – Yellow
300 degree – Magenta
Component refers
to grey level.
Range is [0, 1]
0 means white
1 means black](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colorfundamentalsandcolormodels-210127171226/85/Color-fundamentals-and-color-models-Digital-Image-Processing-22-320.jpg)