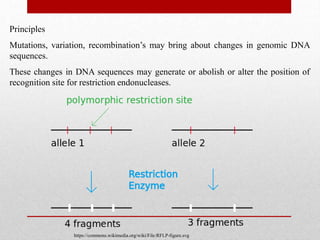
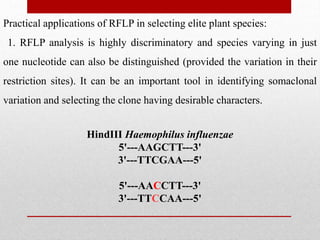
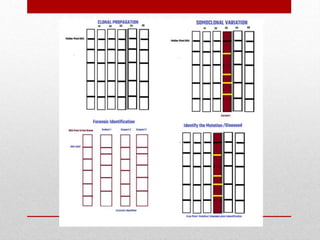
This document discusses Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, which is a technique used to study changes in genomic DNA sequences. RFLP analysis involves digesting genomic DNA from different plant species with restriction enzymes, separating the fragments via gel electrophoresis, and comparing the banding patterns to detect polymorphisms caused by changes in restriction cleavage sites. Some key applications of RFLP analysis mentioned are identifying somaclonal variation to select elite plant clones, detecting genetic disorders at the cellular level, and distinguishing plant varieties and assessing genetic diversity.