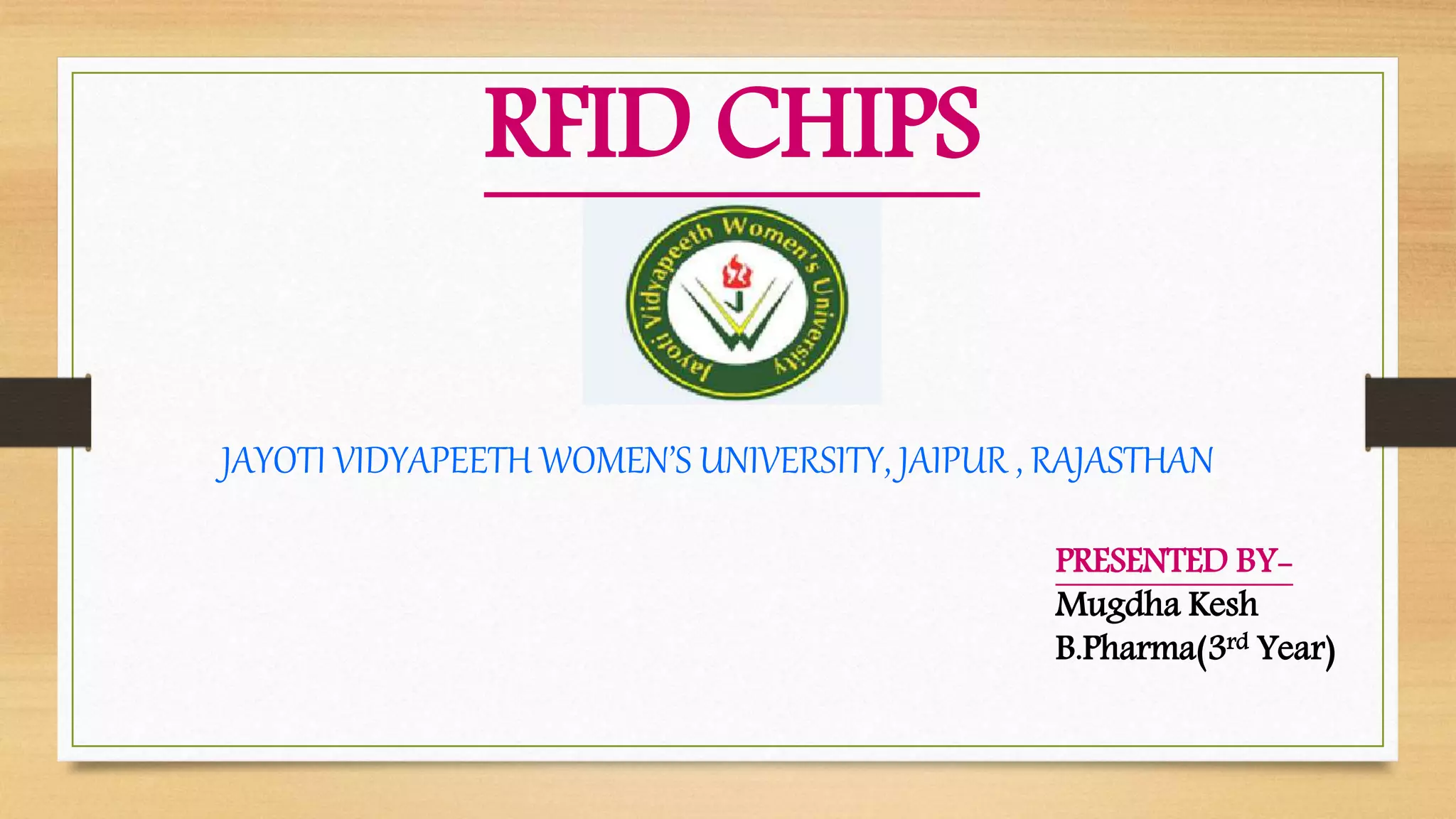
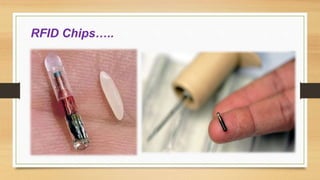
RFID chips use radio waves to automatically identify objects. They contain a microchip antenna that broadcasts a unique identifier to nearby readers. RFID chips can be implanted in humans and used for medical purposes like tracking patients and ensuring they receive the correct medications. While RFID chips provide benefits like easy access to medical histories, there are also risks like tags migrating in the body or potentially causing tumors. Overall, RFID chip technology has applications in healthcare for inventory control, equipment tracking, monitoring patients, and preventing counterfeit drugs.