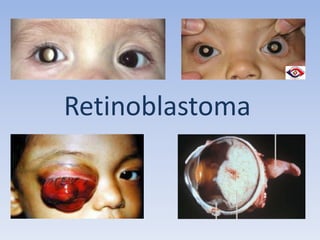
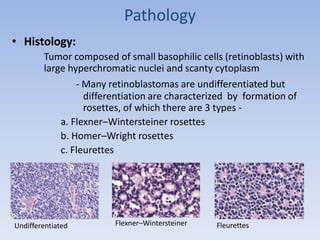
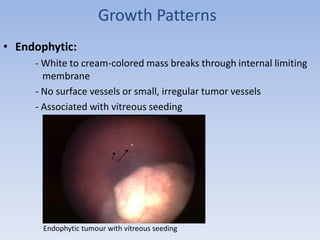
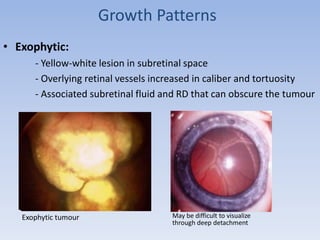
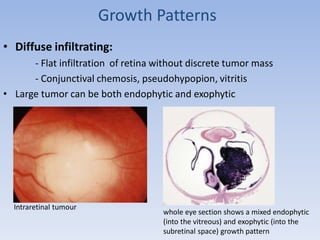
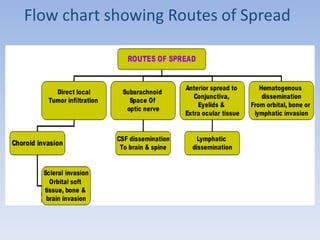
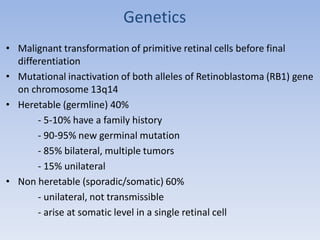
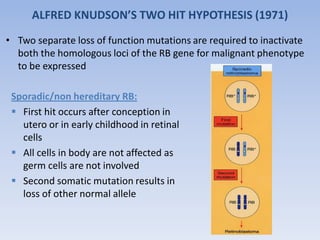
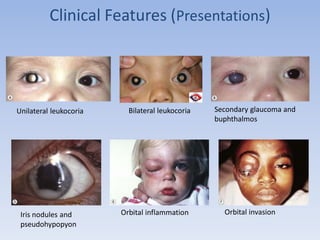
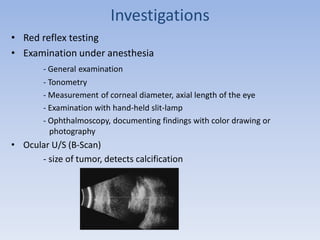
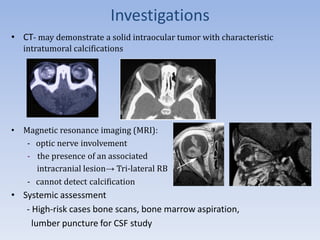
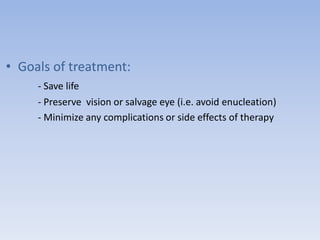
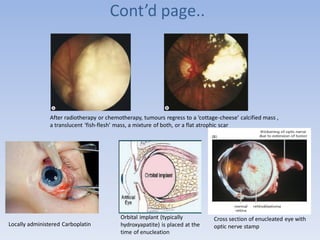
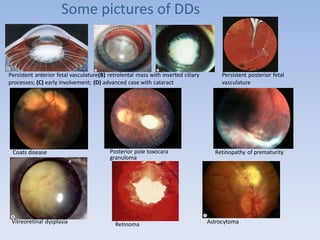
- Retinoblastoma is a rare cancer that affects the retina in young children. It arises from primitive retinal cells.
- The patient was a 19 month old boy referred for a white pupil in the right eye noticed for 4 months. Examination found a white pupil and squint in the right eye.
- Investigations including ultrasound and MRI confirmed the diagnosis of retinoblastoma in the right eye. The family then took the child to another hospital for further chemotherapy and management.