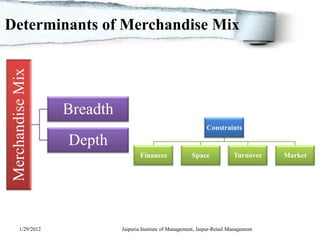
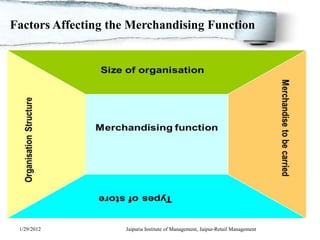
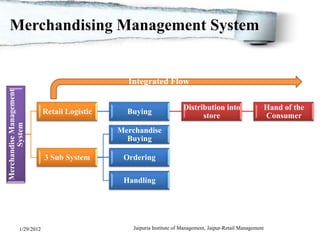
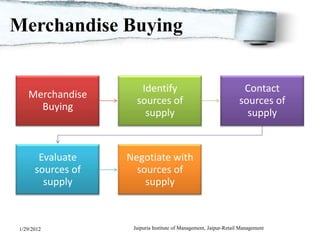
The document discusses retail merchandise management. It describes merchandise management as involving the analysis, planning, acquisition, handling and control of a retail operation's merchandise investments. It outlines several key aspects of retail merchandise management including product assortment planning, buying processes, inventory planning methods, merchandise ordering, handling and visual merchandising. The document provides details on factors that affect merchandising and methods for merchandise planning.





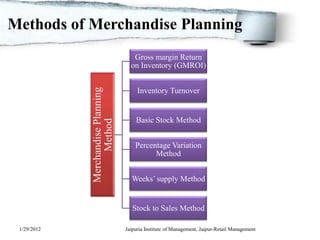



![Methods of Merchandise Planning
Percentage variation method (PVM)
The (PVM) can be calculated as follows:
BOM stock =Average stock for season X ½[1 + (Planned
sales for the month/Average monthly sales)]
1/29/2012 Jaipuria Institute of Management, Jaipur-Retail Management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/retailmerchandisemanagement-120129064949-phpapp01/85/Retail-merchandise-management-13-320.jpg)