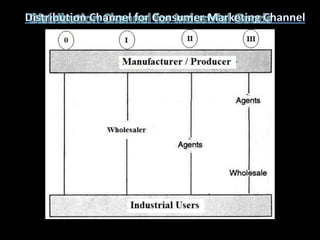
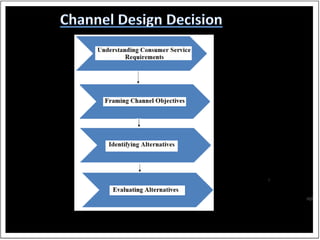
This document discusses distribution channels and sales promotion techniques. It defines distribution channels as the interconnected organizations involved in making a product available to consumers. The objectives of distribution include consumer satisfaction and profitability. It also discusses channel design decisions, functions like order processing and inventory management, and channel management considerations like identifying consumer needs and selecting the optimal channel structure.