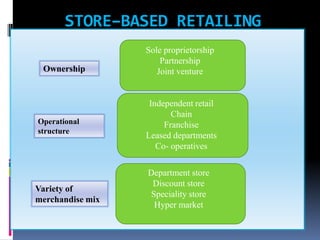
This document classifies and describes different types of retail formats and structures. It discusses store-based retailing which can be sole proprietorships, partnerships, joint ventures, department stores, discount stores, specialty stores, hypermarkets, independent retailers, chain retailers, franchises, and leased departments. It also covers non-store based retailing including direct selling, television shopping, and vending machine retailing.