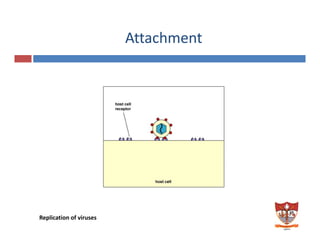
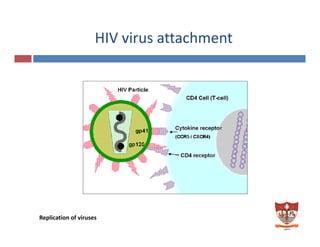
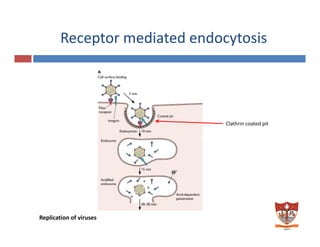
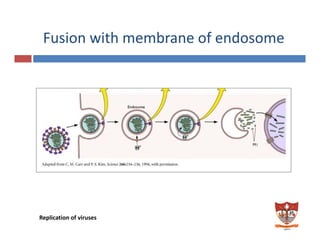
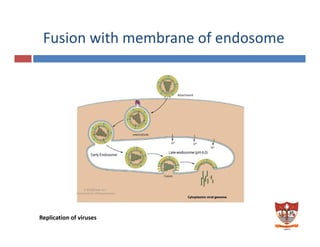
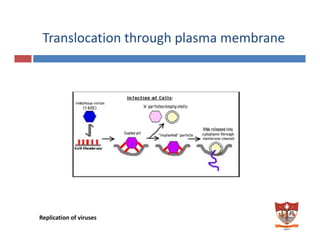
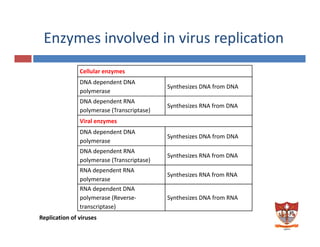
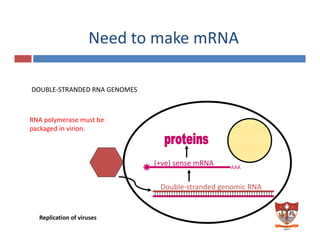
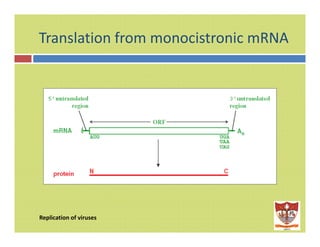
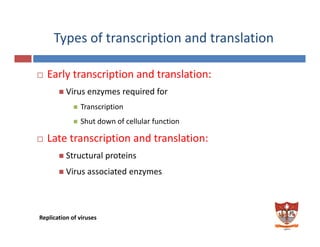
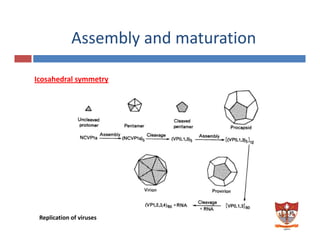
This document discusses the replication of viruses. It describes the key steps in the viral replication process, including attachment to host cells, entry/penetration, uncoating, transcription, translation, replication of the viral genome, assembly, and release. It provides details on the mechanisms and enzymes involved at each step. The replication process allows viruses to multiply inside host cells by using the host's cellular machinery to produce progeny virions.