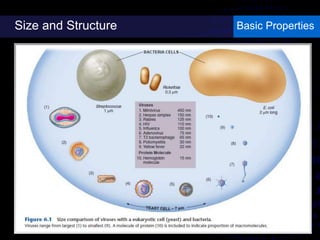
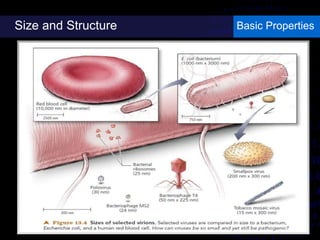
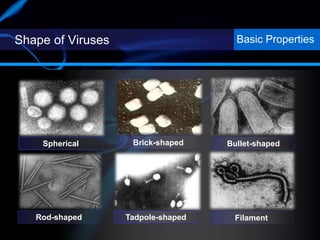
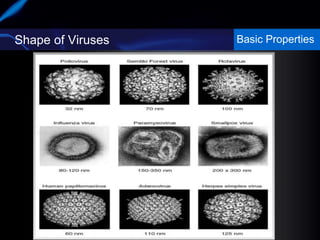
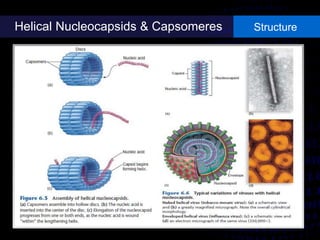
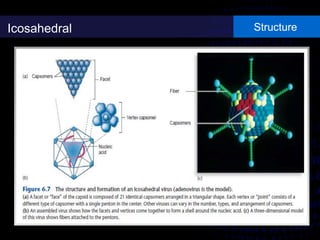
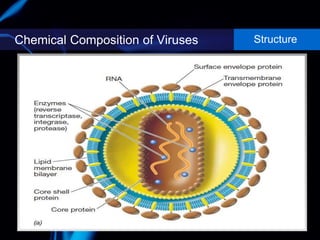
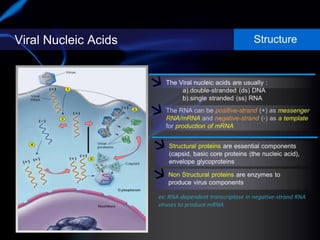
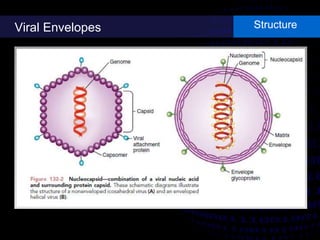
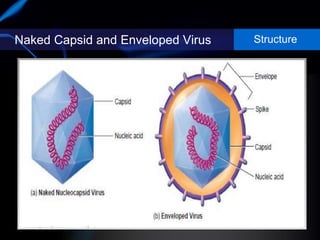
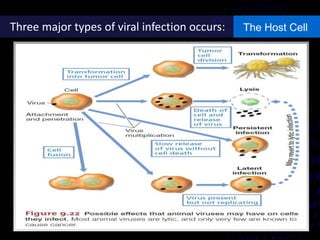
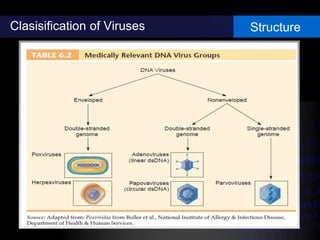
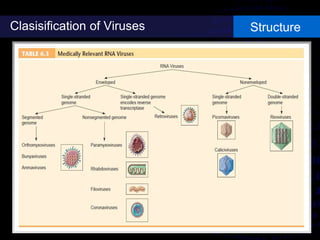
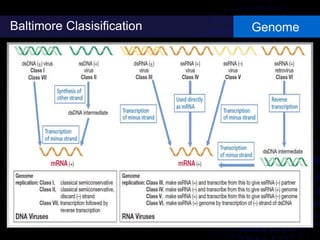
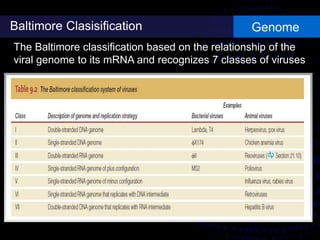
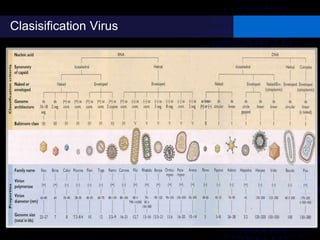
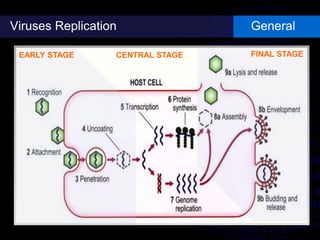
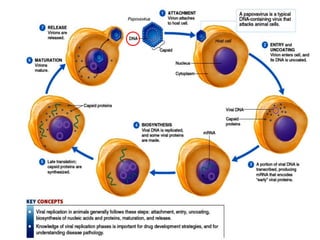
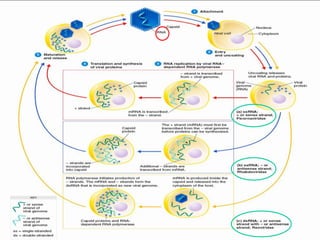
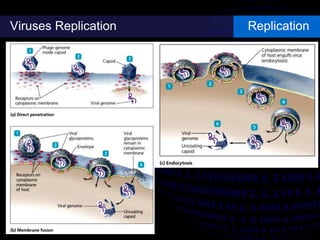
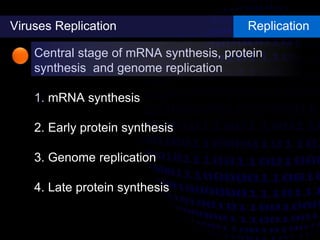
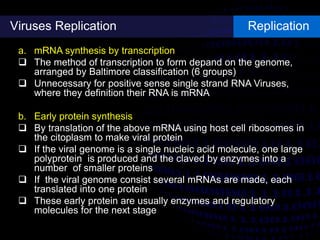
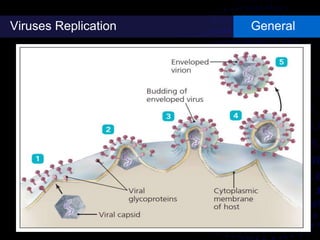
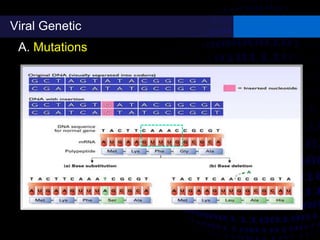
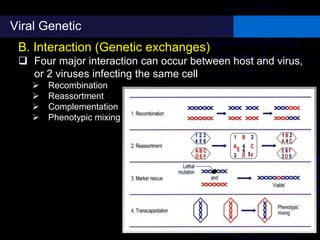
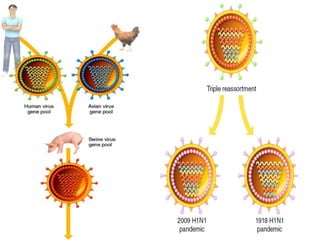
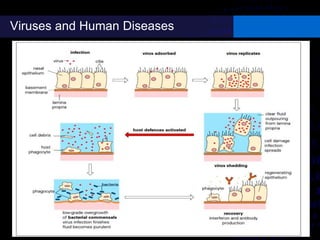
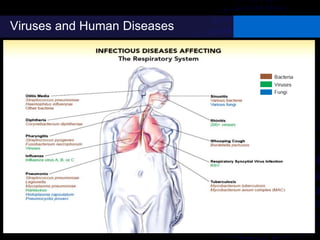
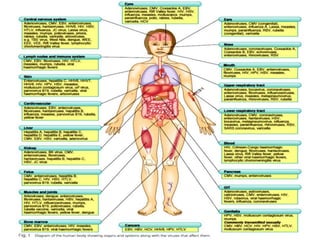
Viruses are small infectious agents that can cause diseases in humans. They replicate inside host cells by using the cell's resources. There are three main stages of viral replication: early, central, and final. In the early stage, viruses attach and enter cells. In the central stage, they produce mRNA, proteins, and genomic material. In the final stage, new virus particles assemble and are released. Viruses can mutate, allowing them to evolve and evade host immune responses. They also interact genetically with each other and their hosts. Viruses cause a wide range of human diseases and conditions, from common colds to cancers.