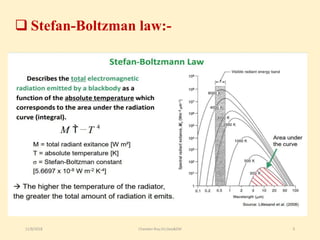
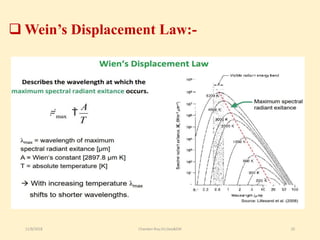
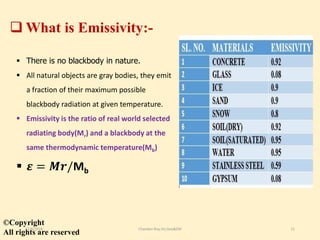
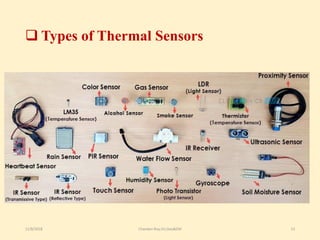
The document discusses thermal remote sensing, emphasizing its role in acquiring and analyzing data from the thermal infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. It covers fundamental concepts such as radiation laws, emissivity, various types of thermal sensors, and a range of applications including environmental monitoring, military applications, and meteorology. The advantages and disadvantages of thermal remote sensing are also highlighted, noting its ability to detect true object temperatures and challenges related to sensor maintenance and image interpretation.