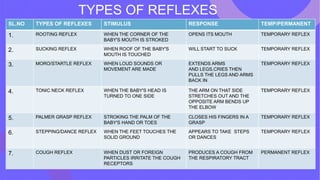
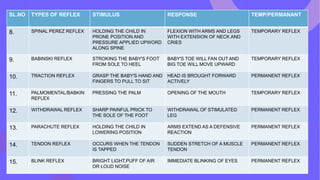
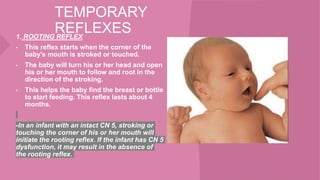
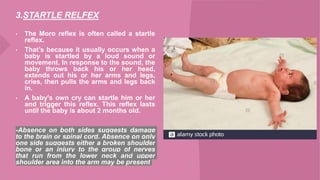
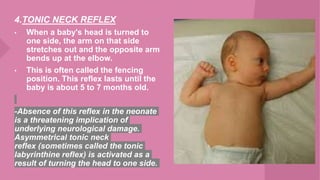
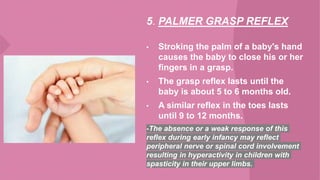
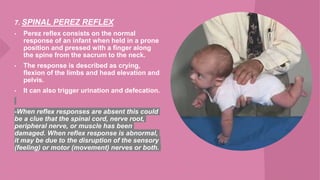
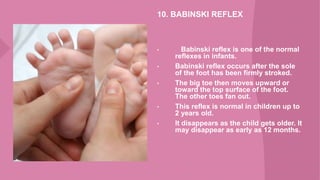
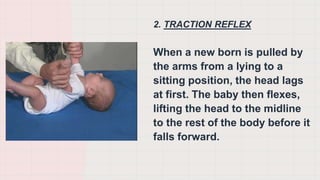
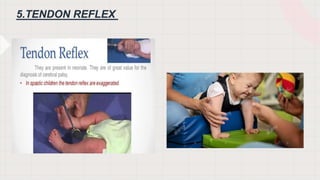
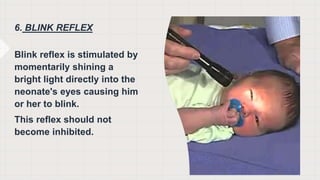
The document discusses neonatal reflexes in newborns. It defines reflexes as involuntary responses to stimuli that do not require conscious thought. It describes 17 different reflexes that are present in newborns, including rooting, sucking, Moro/startle, tonic neck, palmer grasp, stepping/dance, cough, withdrawal, parachute, tendon, and blink reflexes. The reflexes are categorized as either temporary reflexes that disappear during the first year or permanent reflexes that remain throughout life. The document provides details on the stimulus and response for each reflex and their implications for development.