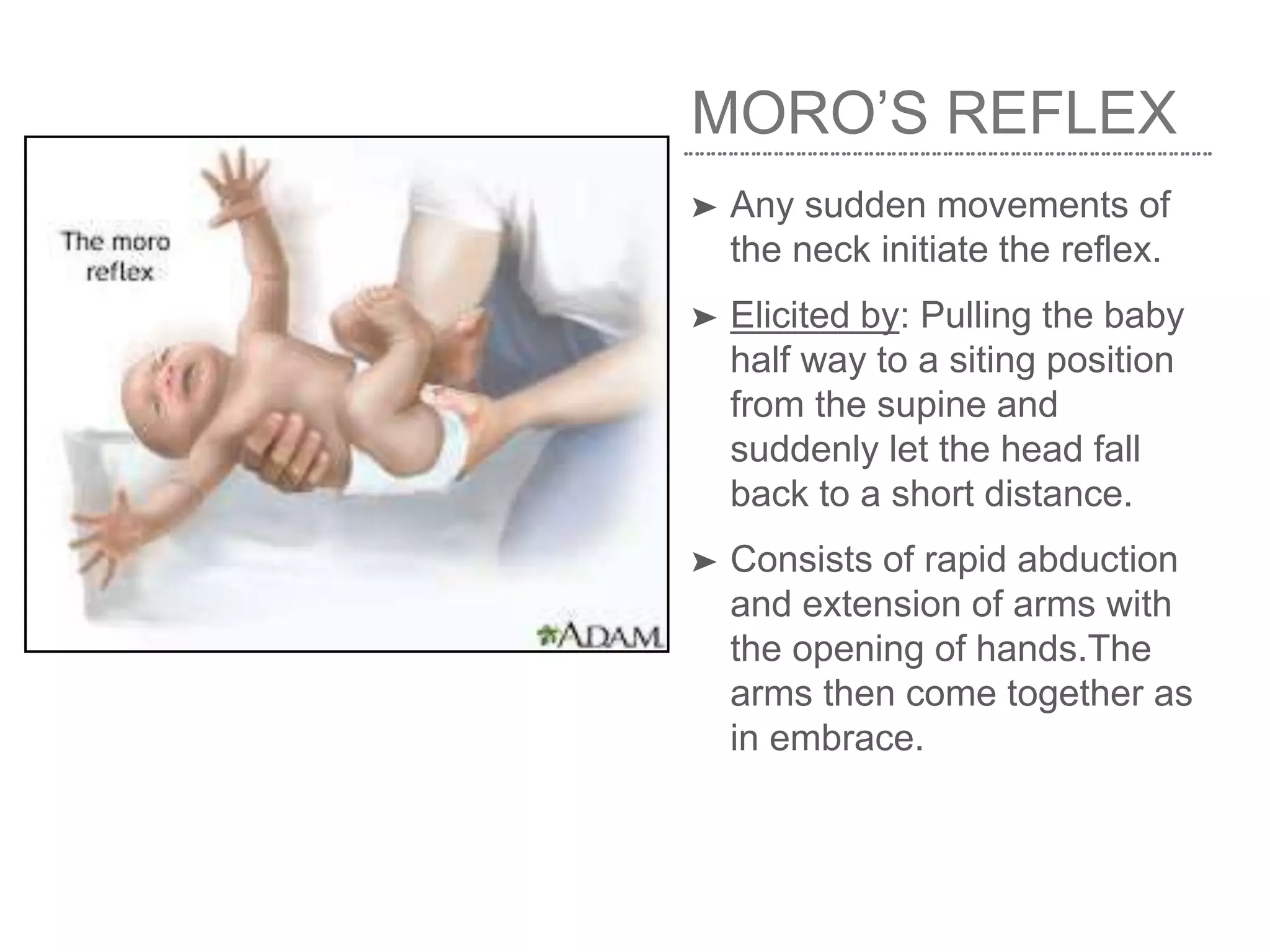
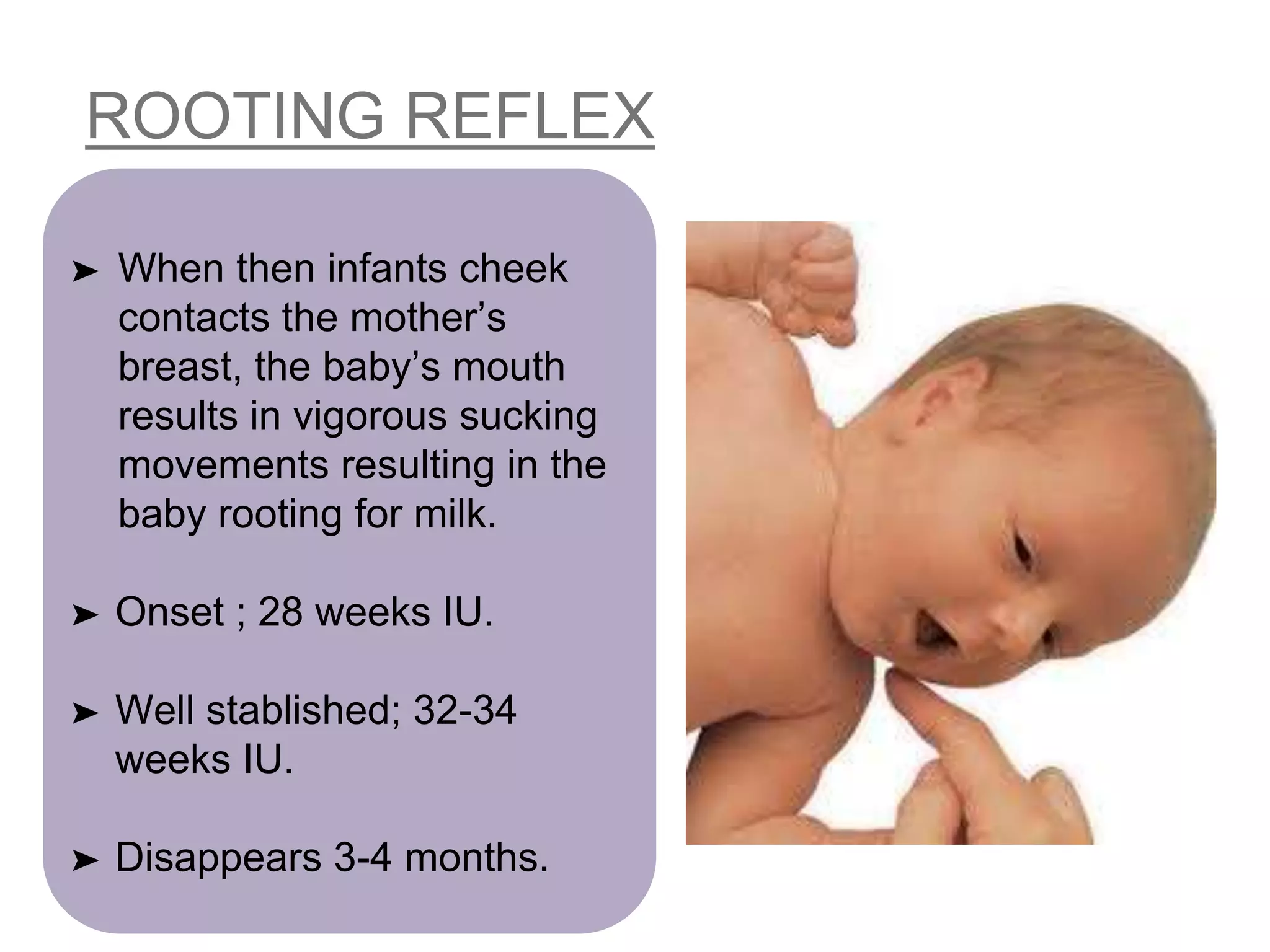
This document defines and describes various neonatal reflexes seen in newborns and infants. It outlines general body reflexes including Moro, palmer/grasp, and Babinski's reflexes. It also discusses facial reflexes such as blink, doll's eye, and corneal reflexes. Finally, it examines oral reflexes including rooting, sucking, and gag reflexes. These primitive reflexes are present at birth and disappear over the first year as the nervous system develops and matures. Their presence indicates normal neurological development in infants.