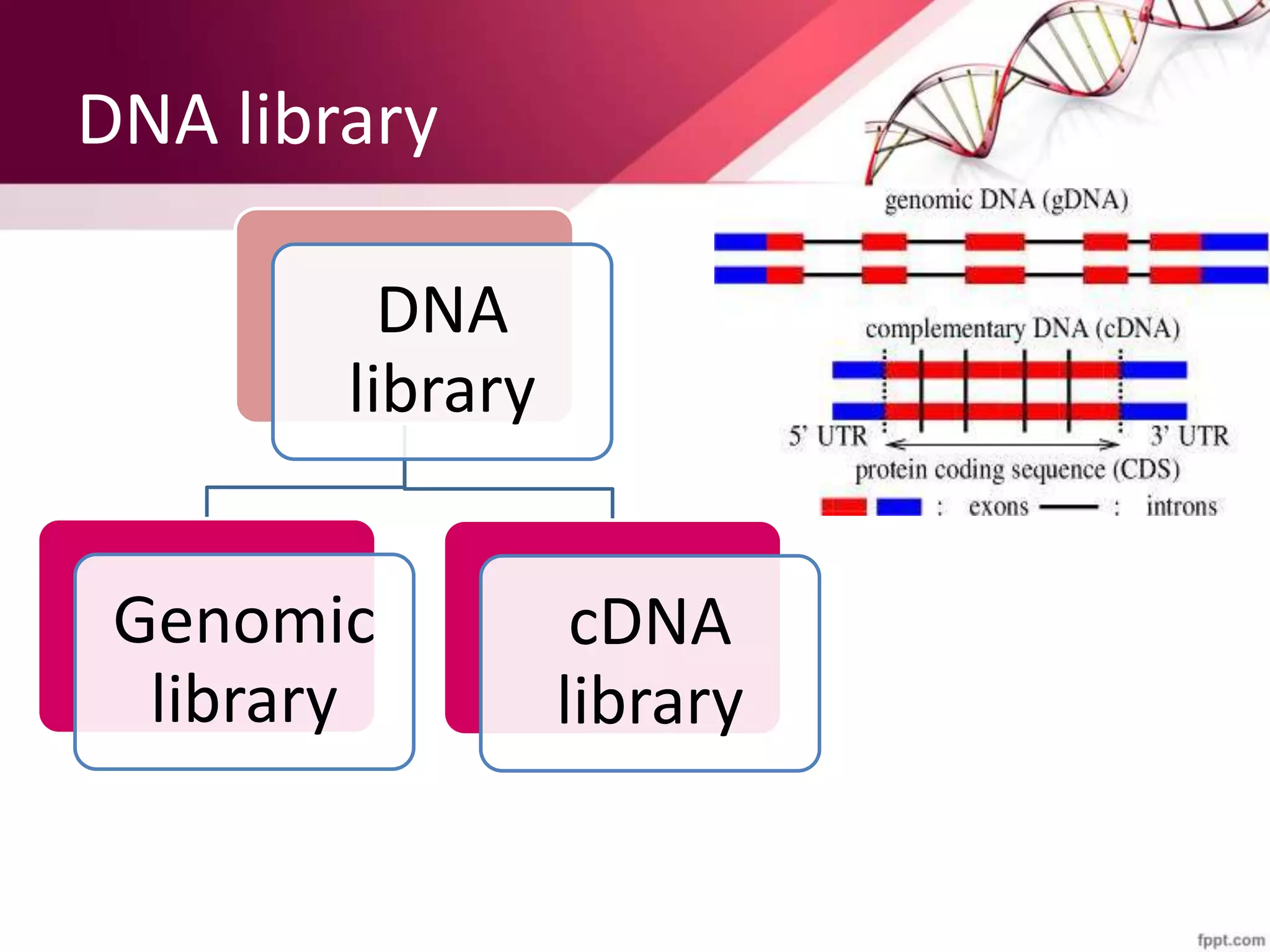
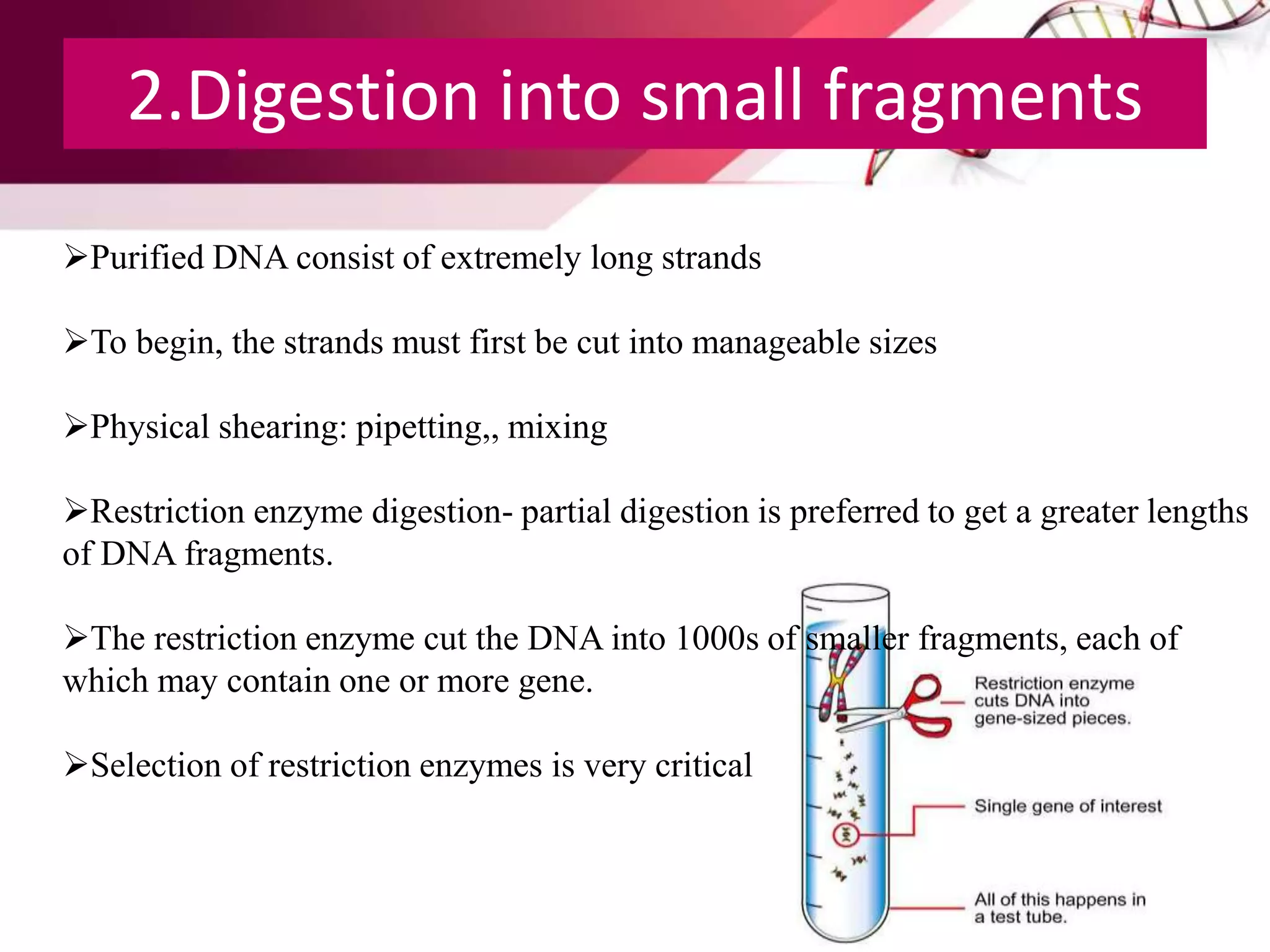
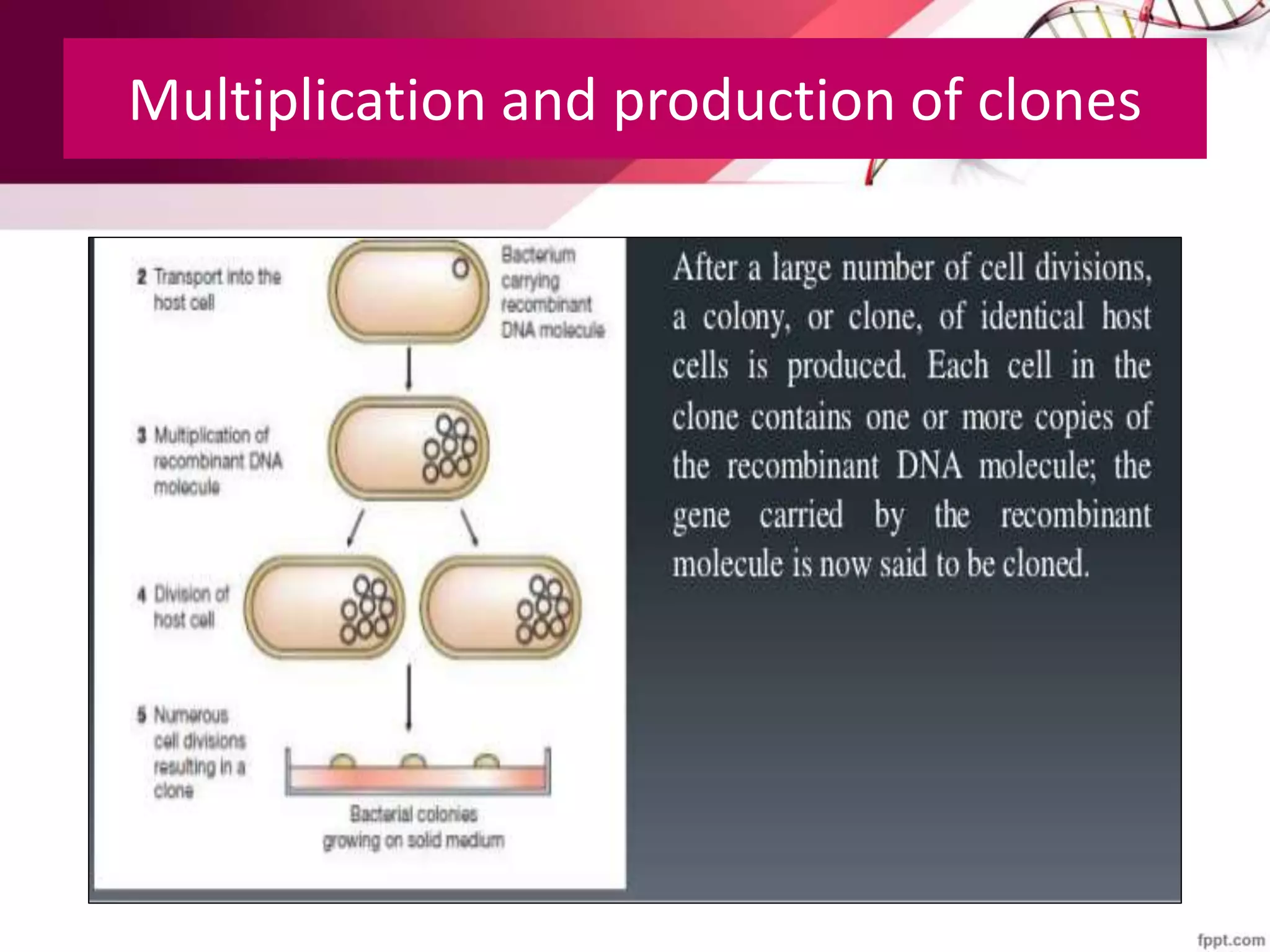
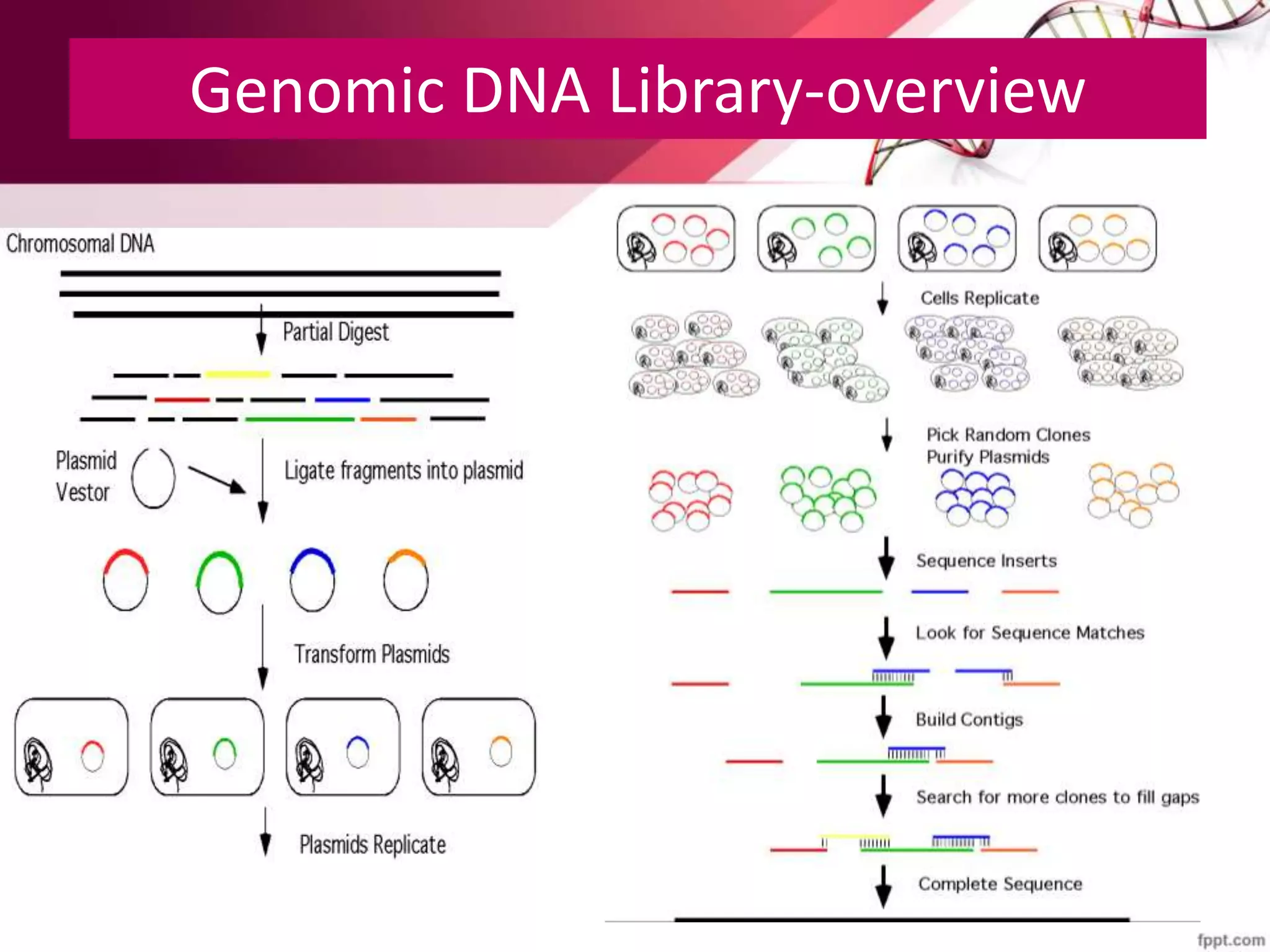
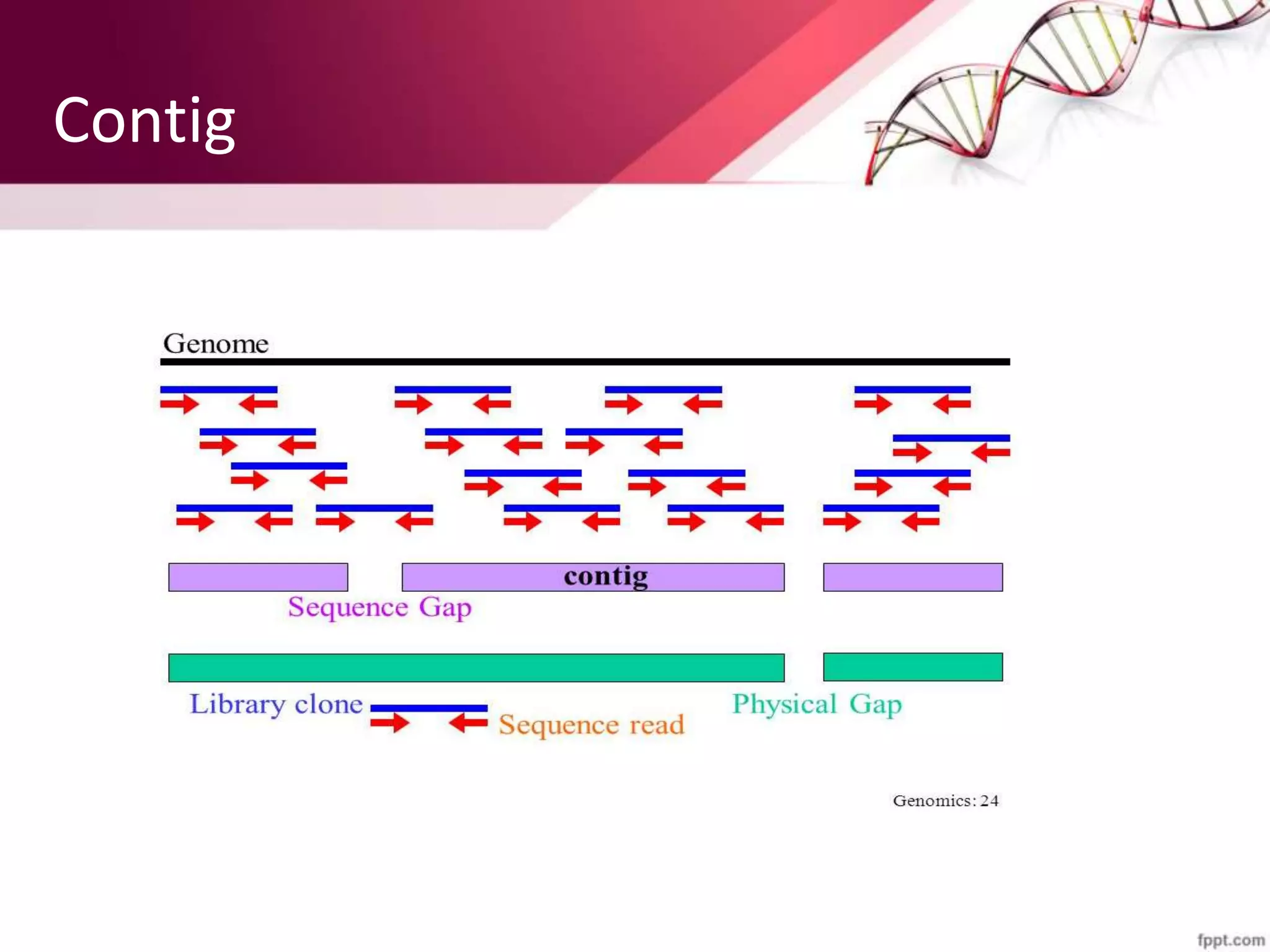
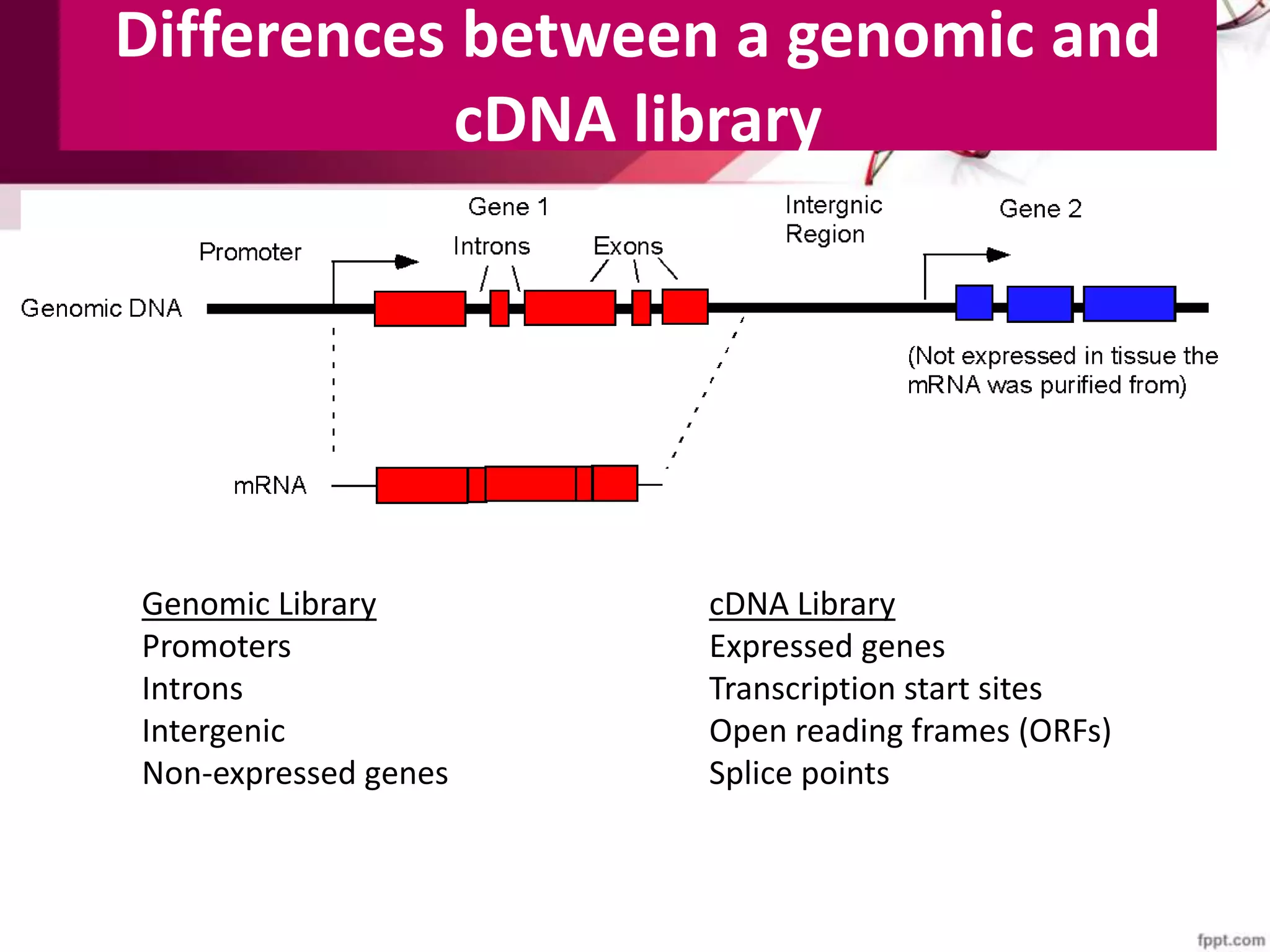
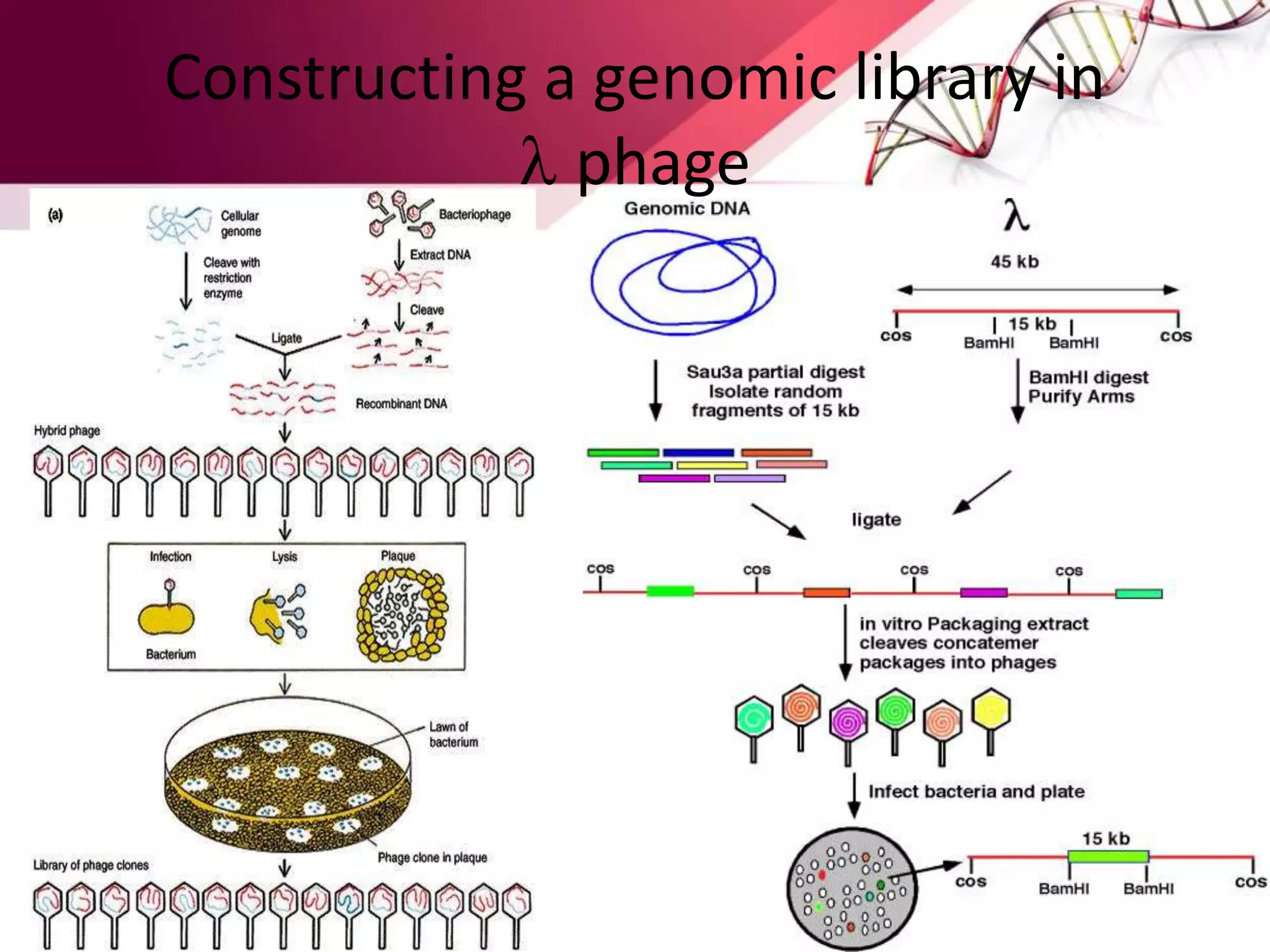
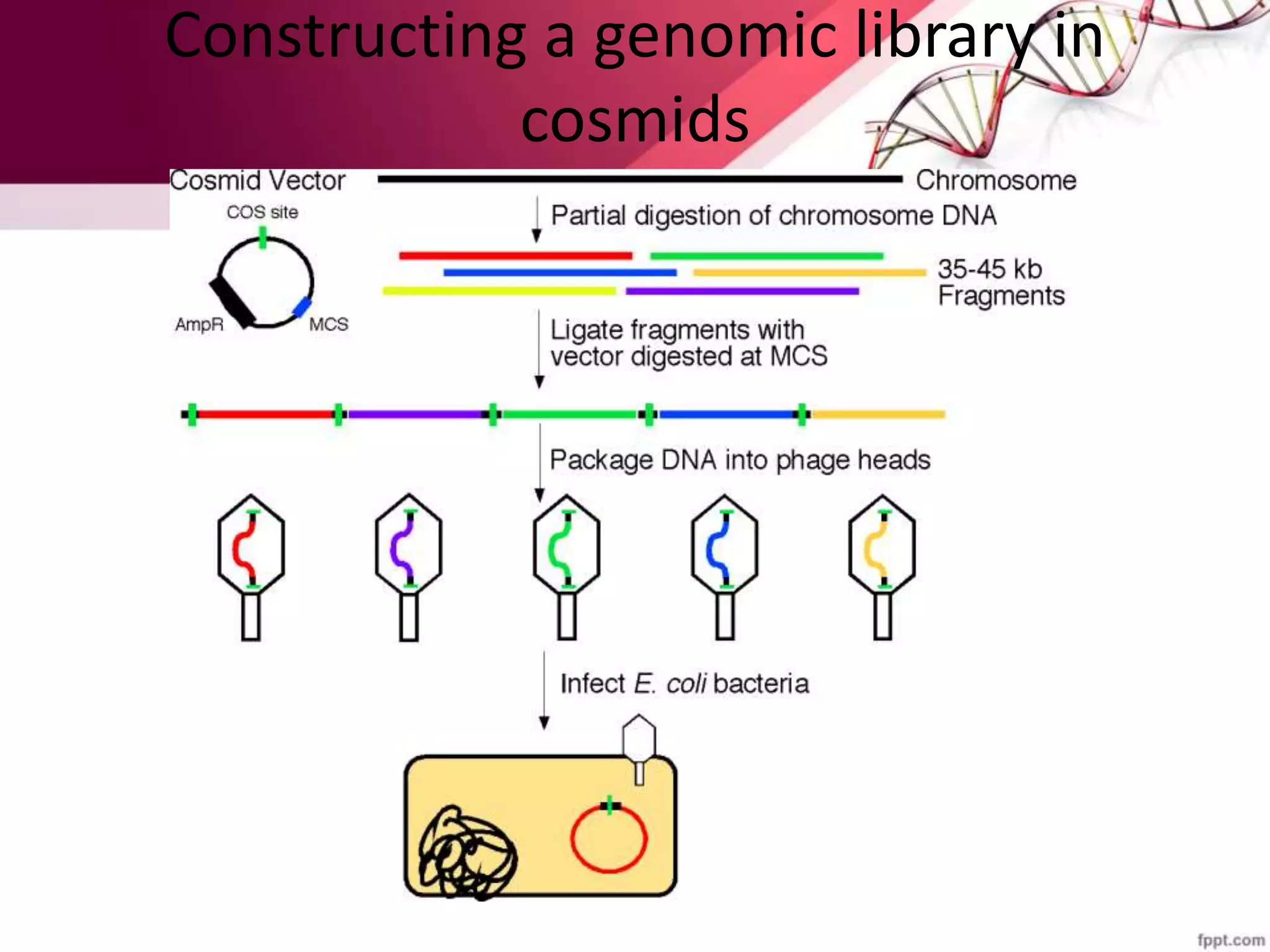
A DNA library is a collection of DNA fragments that have been cloned into vectors. DNA libraries allow researchers to isolate and study specific DNA fragments of interest. To create a genomic library, DNA is extracted from an organism, cut into fragments, inserted into vectors, and introduced into host bacteria to generate clones containing all the organism's DNA sequences. This library can then be screened to identify and study particular genes. DNA libraries provide an efficient way to store, isolate, and analyze DNA sequences.