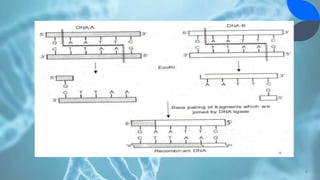
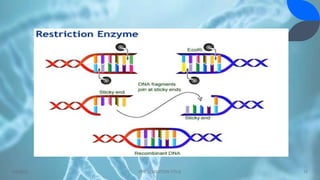
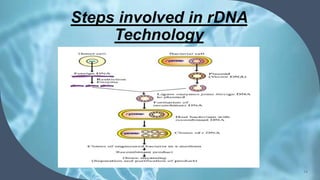
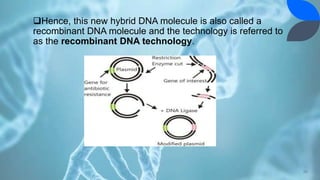
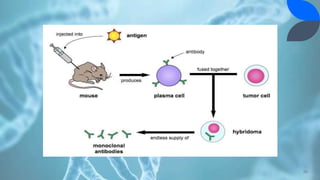
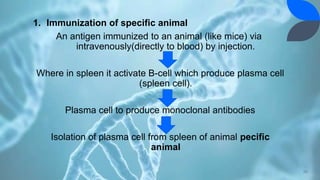
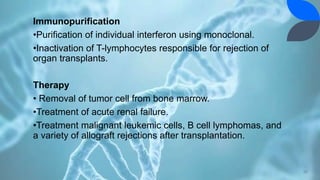
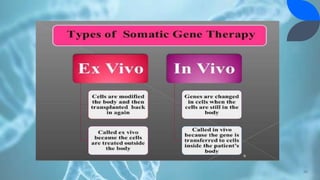
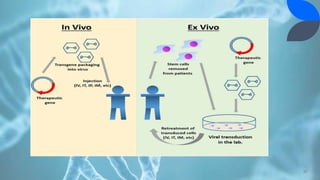
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology involves combining DNA molecules from different sources into new combinations. DNA from one organism is cut and joined with DNA from another organism, and the resulting recombinant DNA is inserted into a host cell. This allows genes and DNA fragments to be expressed, amplified, and mass produced. The basic steps are isolation of genetic material, restriction enzyme digestion, amplification via PCR, ligation, insertion into a host cell, and isolation of recombinant cells. rDNA technology has many applications including basic research, production of therapeutic proteins, agriculture, medicine, and industry. Hybridoma technology uses cell fusion to produce monoclonal antibodies that are identical clones of a single parent cell.